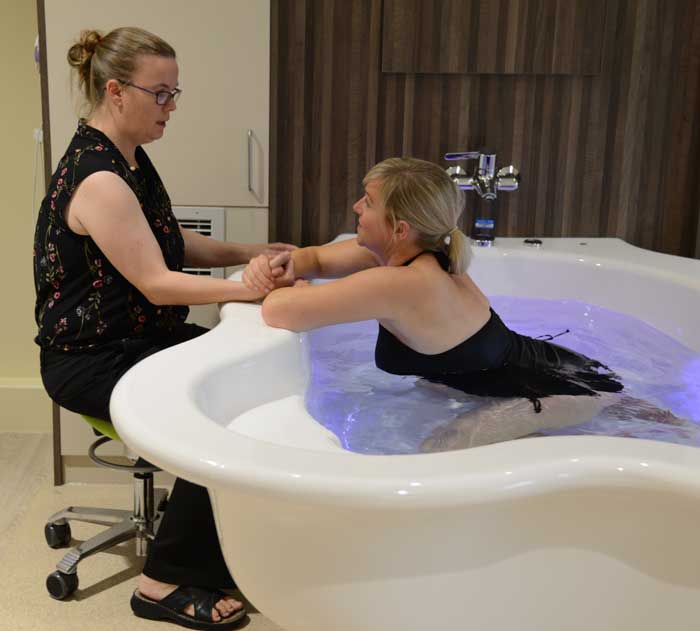
Water births provide “clear benefits” over standard care for healthy mothers and their newborns, according to UK researchers.
They found water births were associated with fewer interventions and complications during and after the birth, as well as higher levels of satisfaction for the mother.
“Water immersion is an effective method to reduce pain in labour, without increasing risk”
Study authors
Researchers compared the extent of healthcare interventions needed during and after labour to see if outcomes differed between a water birth and standard care – without a birthing pool.
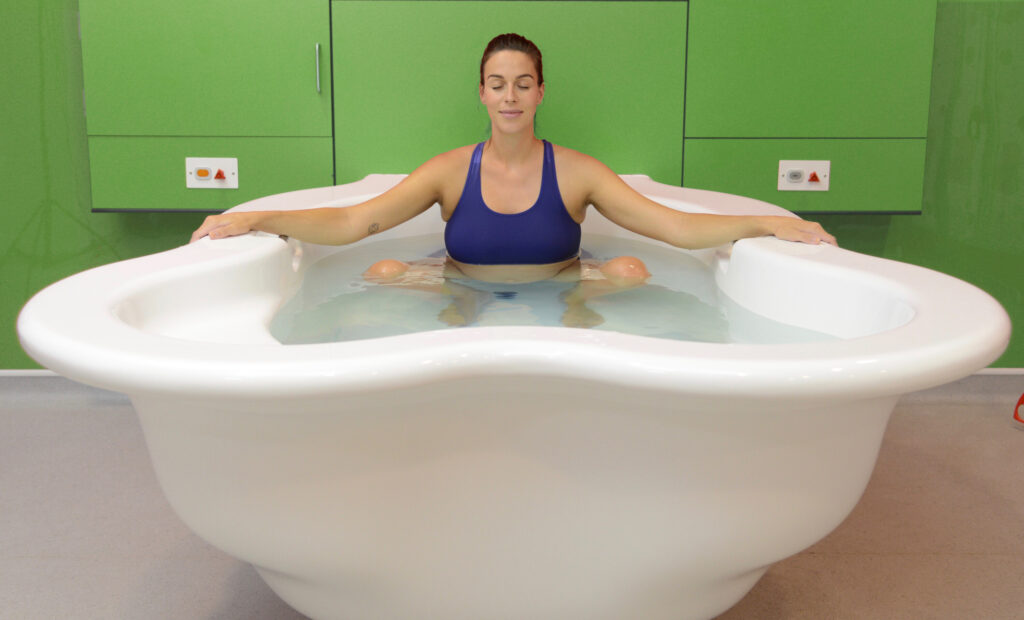
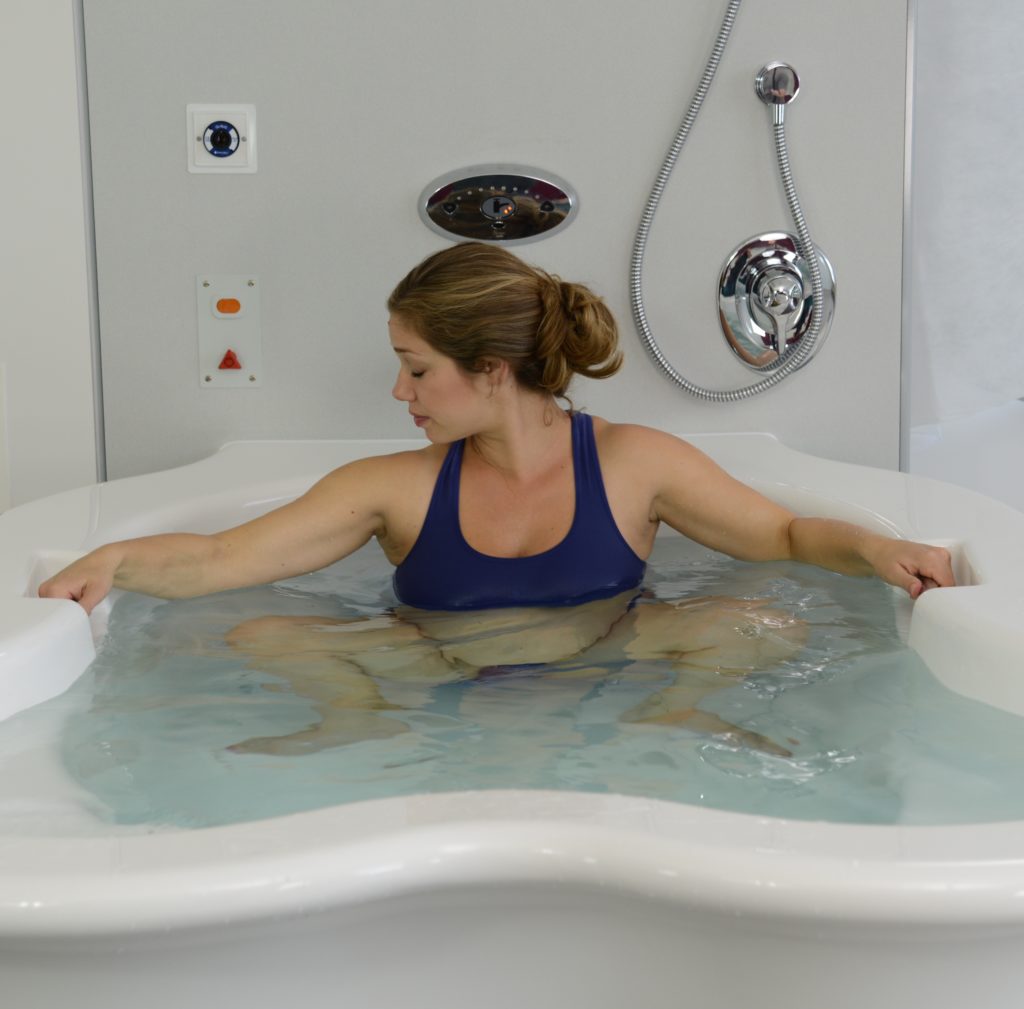
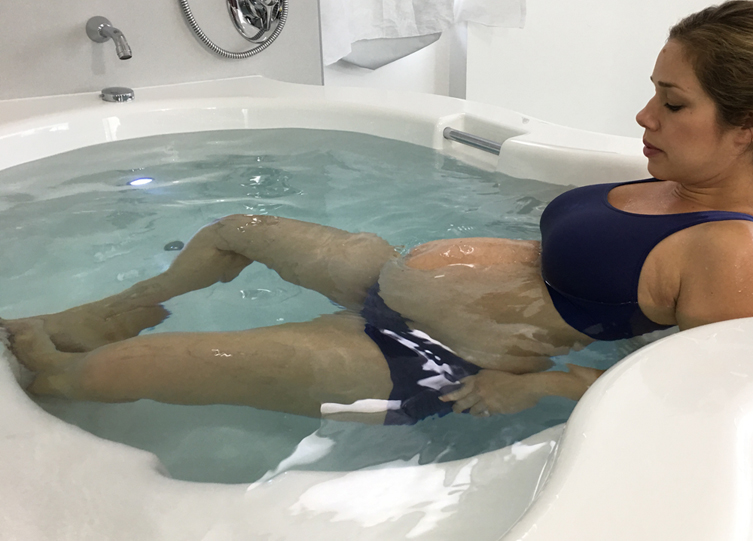
They noted that a water birth involves using a birthing pool to achieve relaxation and pain relief, with the mother either exiting the pool for the birth, so the newborn can emerge into air to breathe, or remaining in the pool and bringing the newborn to the surface to start breathing.
They trawled research databases looking for relevant studies published over 20 years between 2000 and 2021, finding 36 studies involving 157,546 women. Most were carried out in obstetric units.
The study results showed that a water birth, regardless of whether women birth in or out of the pool, “has clear benefits to women” in obstetric units, where most births take place and where interventions and complications are more likely than in midwife-led units.
A waterbirth was as safe as standard care for healthy mothers and their newborns, they said in the journal BMJ Open.
Compared with standard care, a water birth significantly reduced the use of epidurals, injected opioids, episiotomy, as well as pain and heavy bleeding after the birth.
In addition, it increased mothers’ satisfaction levels and the odds of an intact perineum. There was no difference in the rate of Caesarean sections, said the study authors from Oxford Brookes University.
“Water immersion can significantly increase the likelihood of an intact perineum and reduce episiotomy, an intervention which offers no perineal or foetal benefit, can increase postnatal pain, anxiety, and impact negatively on a woman’s birth experience,” they said.
However, they observed more instances of umbilical cord breakage among water births, but the rate was still low – 4.3 per 1,000 births in water compared with 1.3 per 1,000 births with standard care.
This finding may be linked to pulling on the umbilical cord when the newborn is brought up out of the water, the researchers suggested.
Overall, they stated: “Water immersion provides benefits for the mother and newborn when used in the obstetric setting, making water immersion a low-tech intervention for improving quality and satisfaction with care.
“In addition, water immersion during labour and waterbirth alter clinical practice, resulting in less augmentation, episiotomy, and requirements for pharmacological analgesia,” they said.
They concluded: “Water immersion is an effective method to reduce pain in labour, without increasing risk.”
However, they acknowledged that information on birth settings, care practices, interventions and outcomes varied considerably among the included studies, and few were carried out in midwife-led units or in the mother’s home, which may have affected the findings of the analysis.
To strengthen the evidence base, future research should include factors that are known to influence interventions and outcomes during and after labour or birth, they added.
For example, how many children a woman has already had, where she gives birth, who looks after her, and the care she receives.
“The challenge now is to ensure this choice is open to all women wherever they live”
Clare Livingstone
Commenting on the research, Clare Livingstone, professional policy advisor at the Royal College of Midwives, said: “This is really good news for women choosing to have a water birth or thinking of having one.
“There has been previous research outlining the benefits for women and this significant study adds weight to those. It is also positive because it is more information for women when deciding how they want to give birth.”
She said: “Water births are becoming more widely available for women across the UK, but this isn’t the case everywhere. The challenge now is to ensure this choice is open to all women wherever they live.”
Ms Livingstone added: “What is needed now is to see more research into water births in midwife-led settings and in women’s homes. This will give us a broader picture of the impact of water births.”