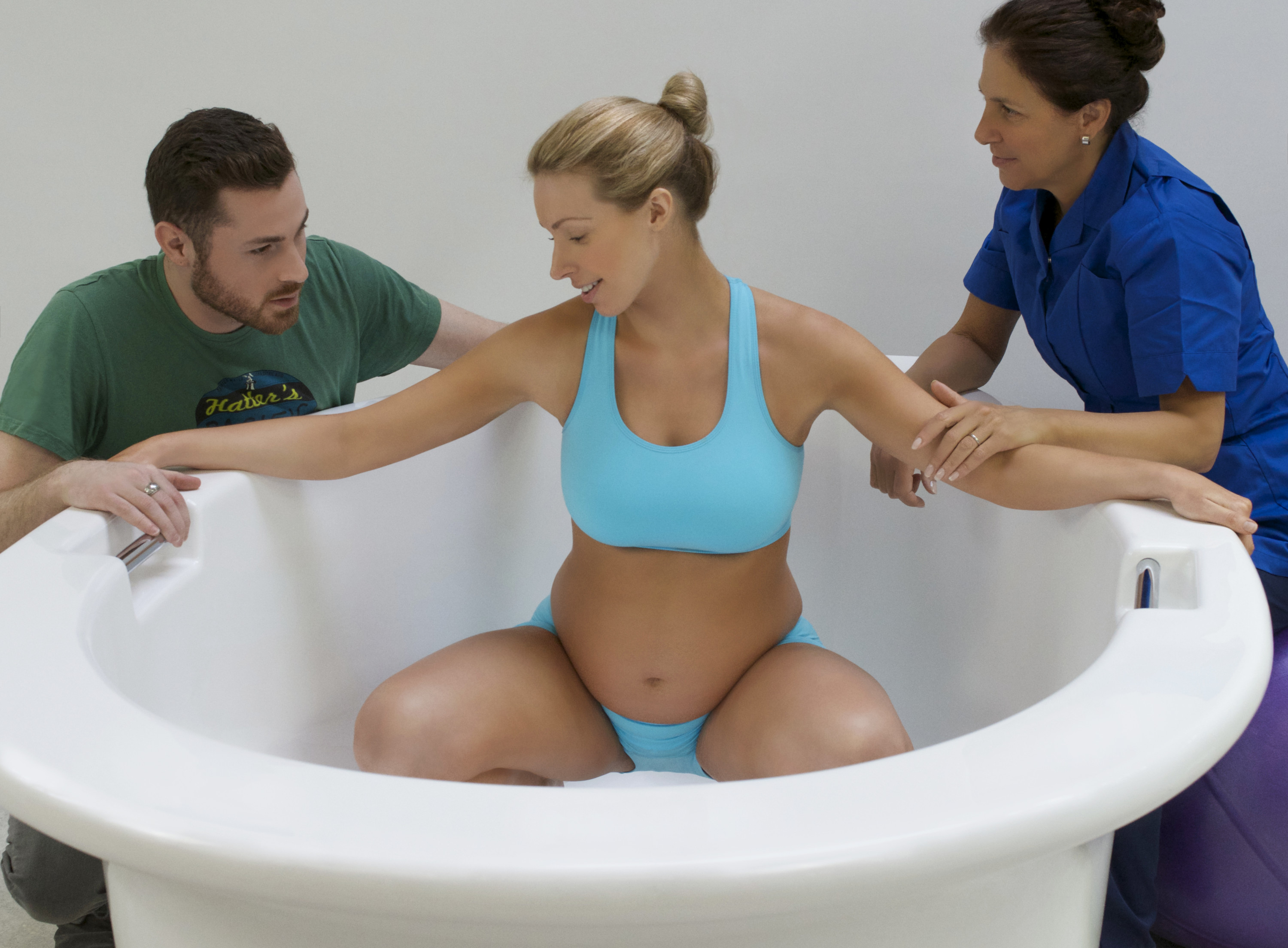
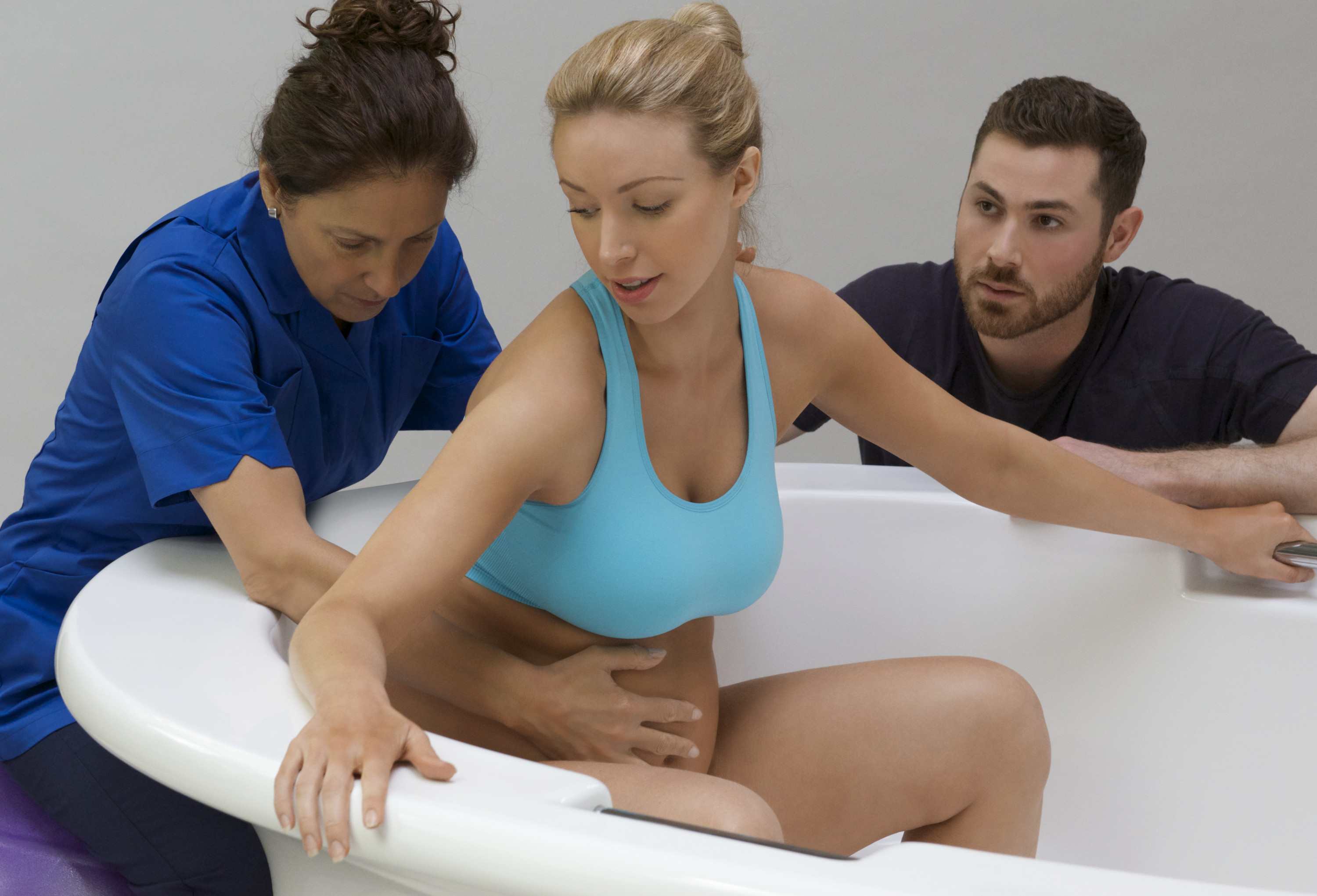
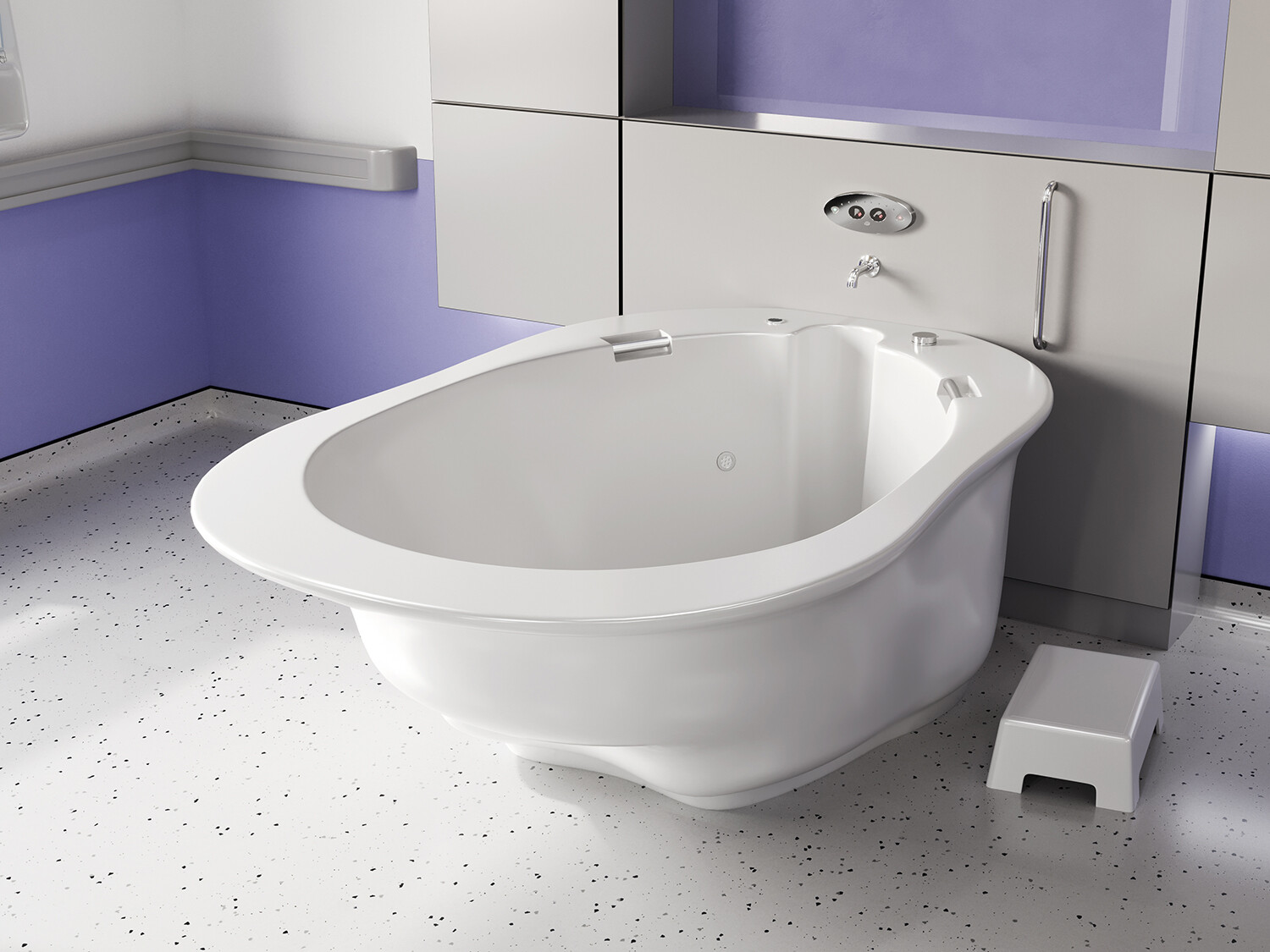
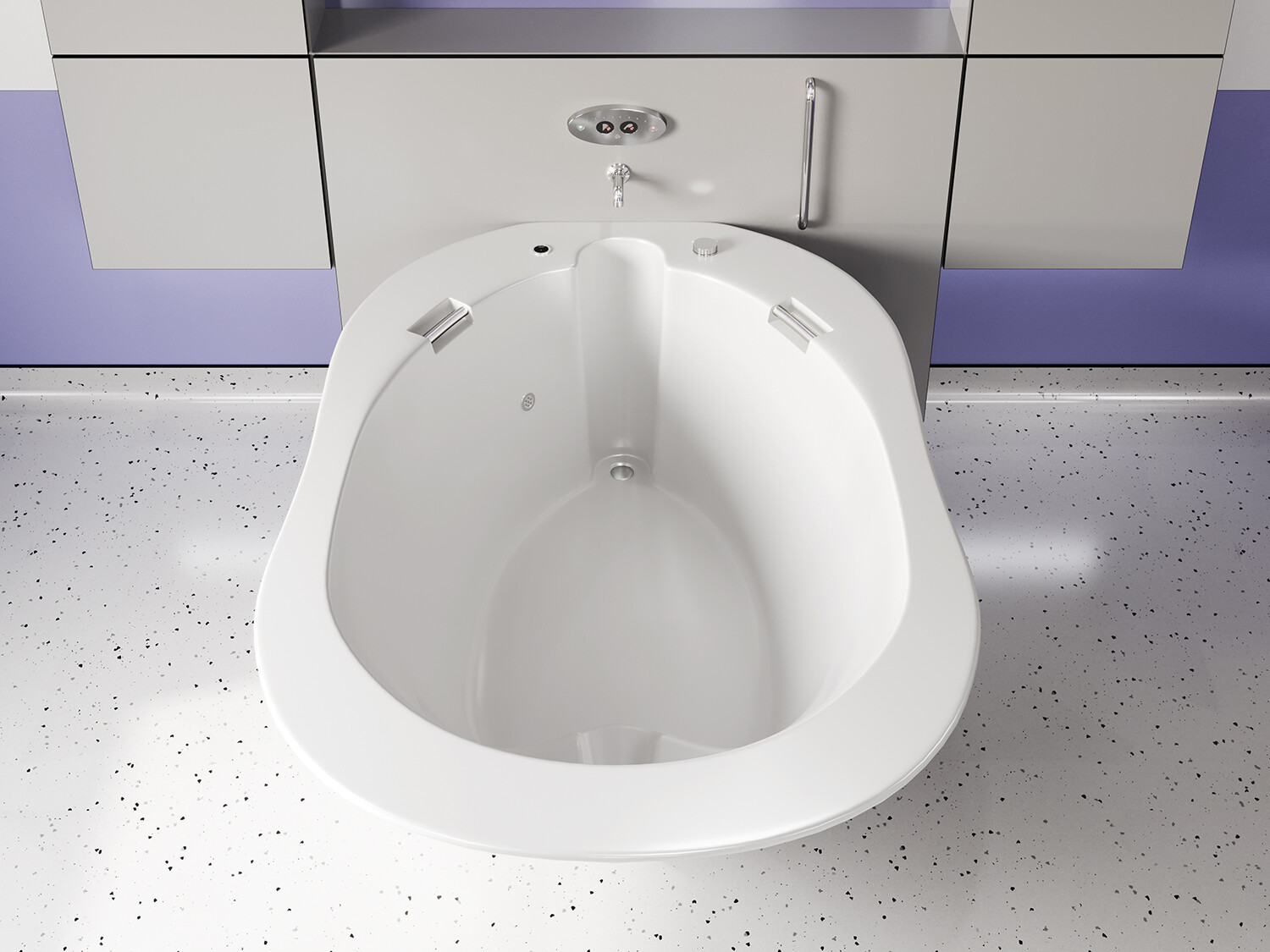
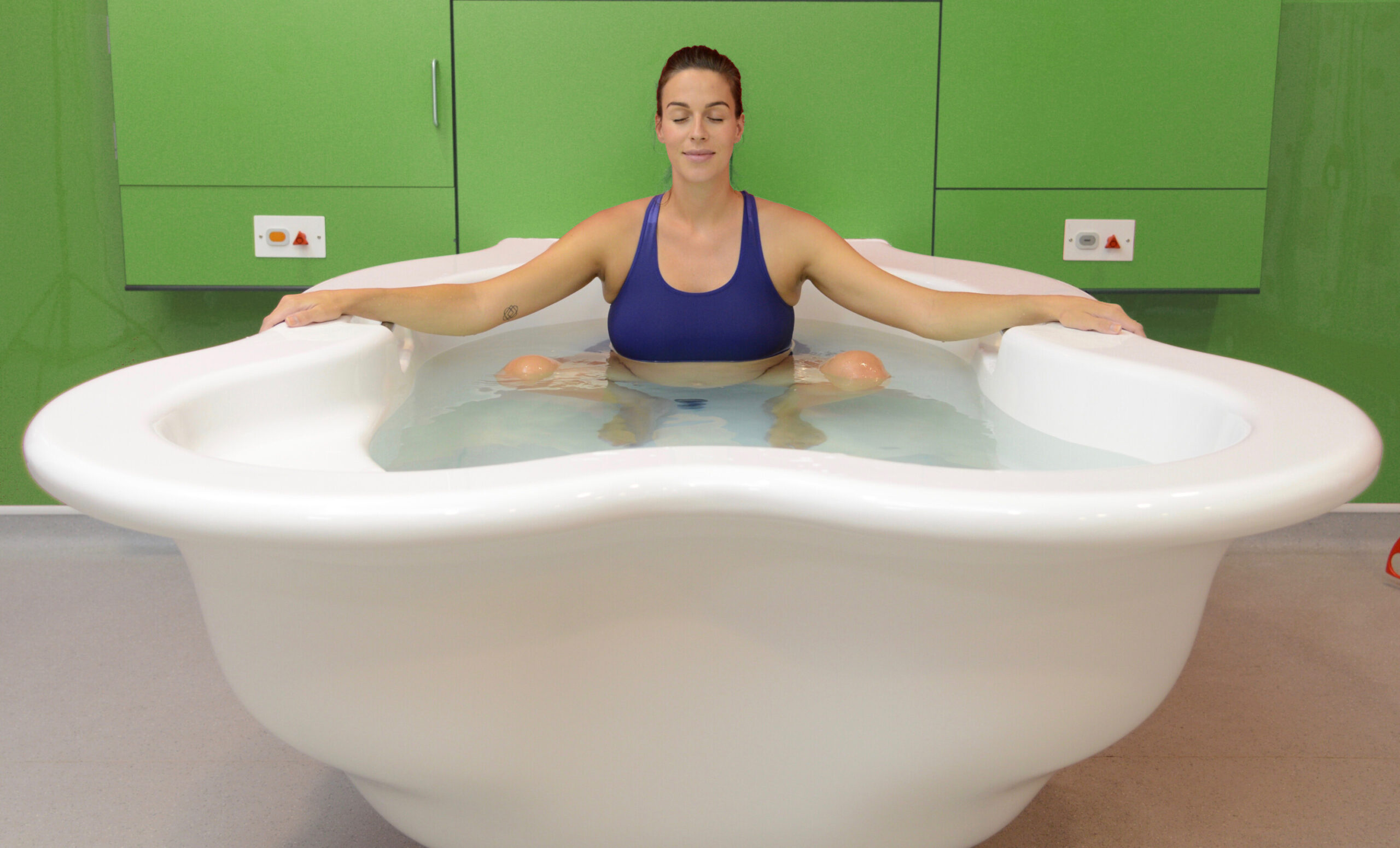
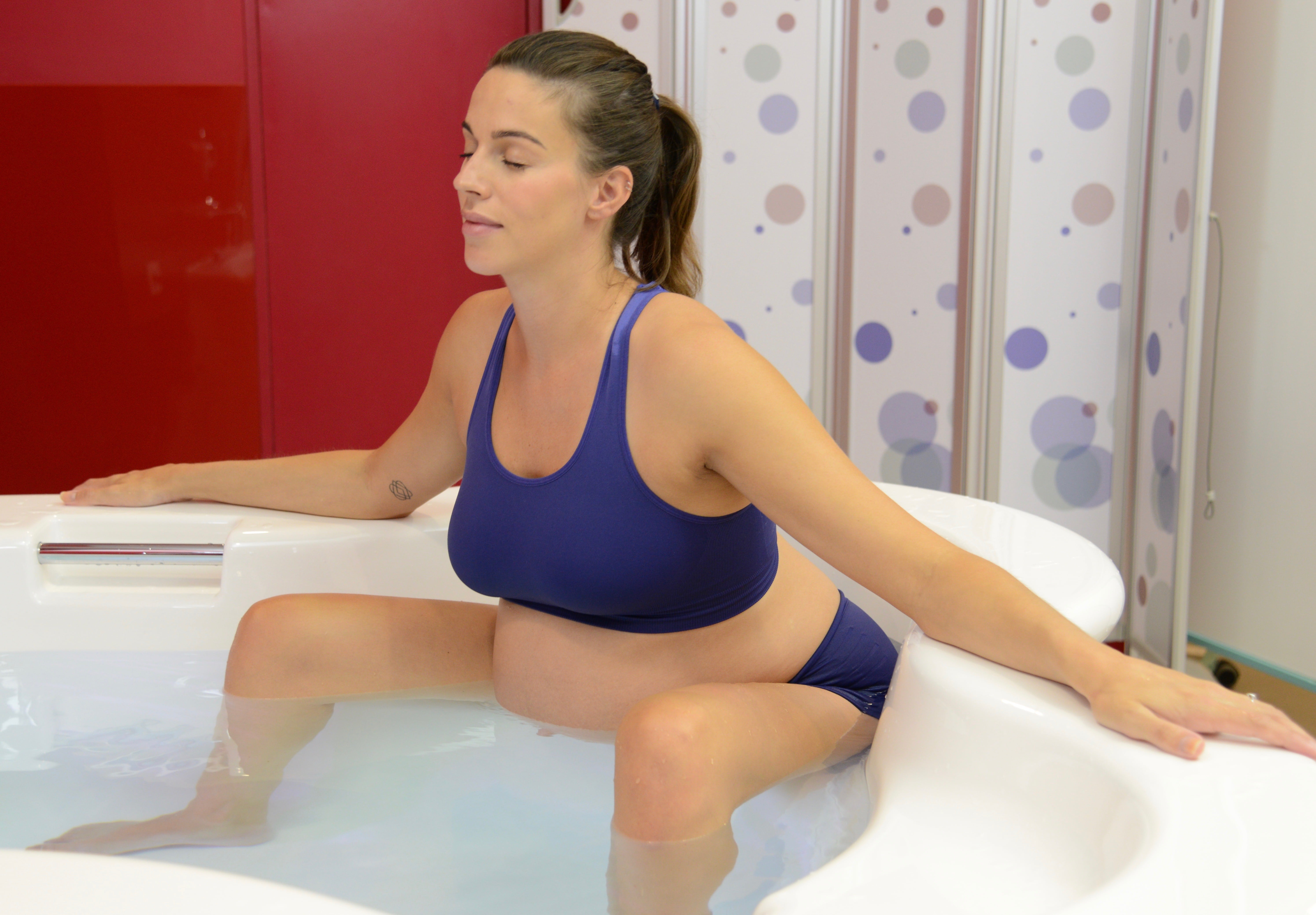
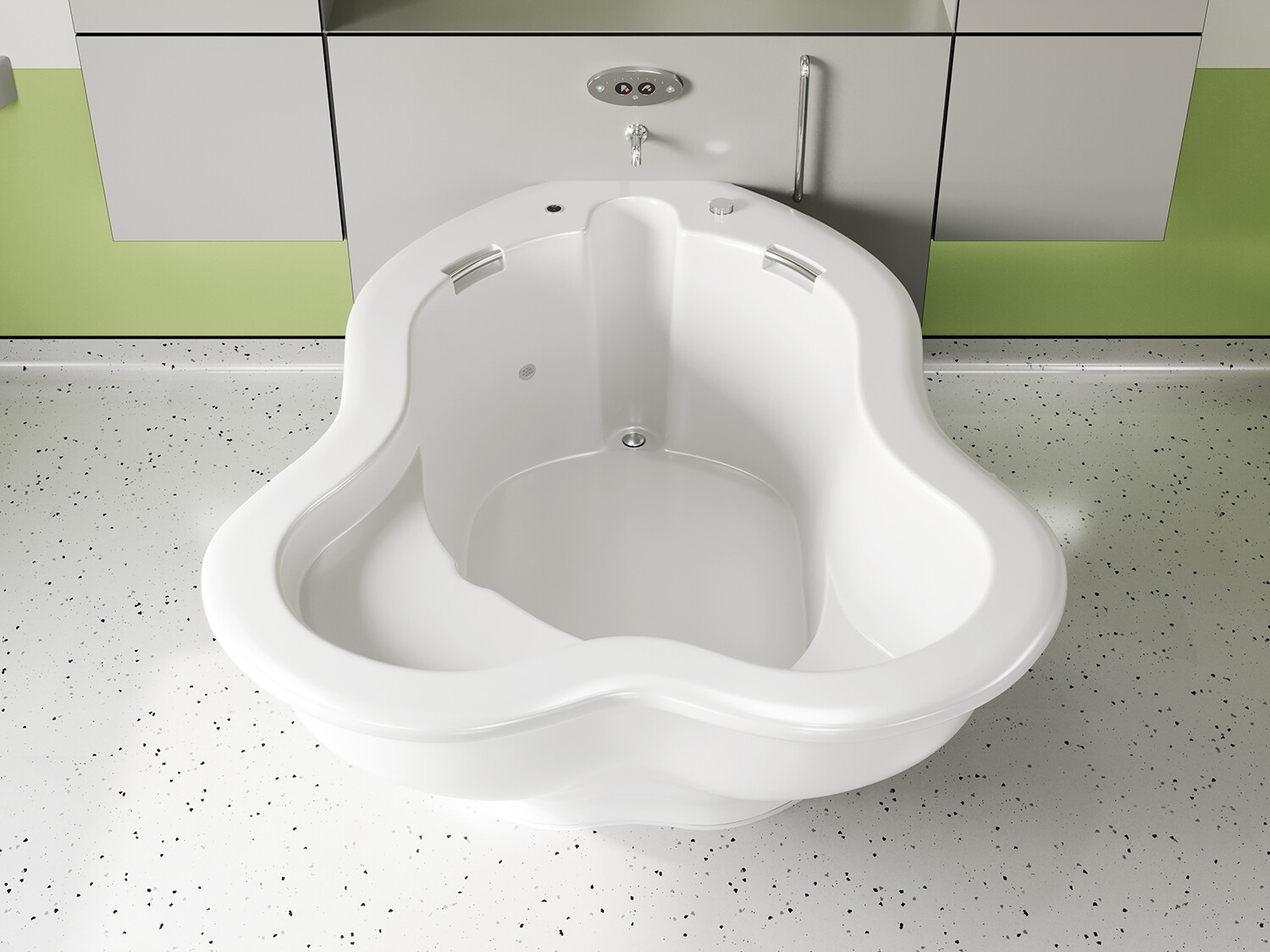
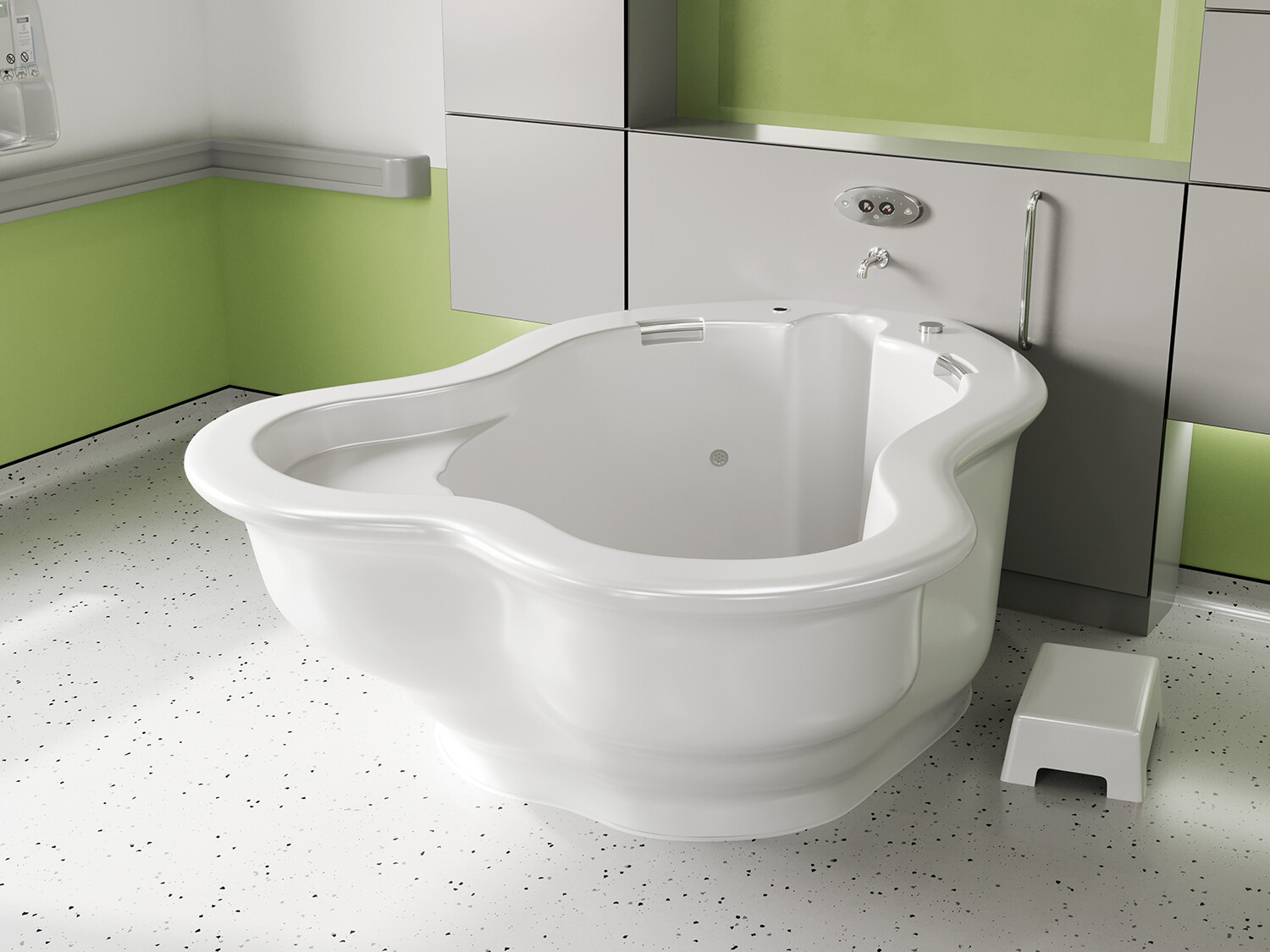
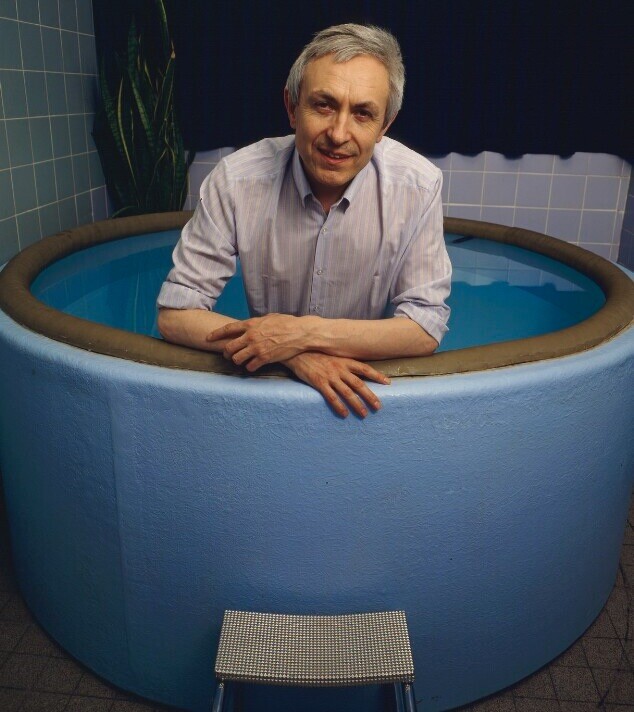
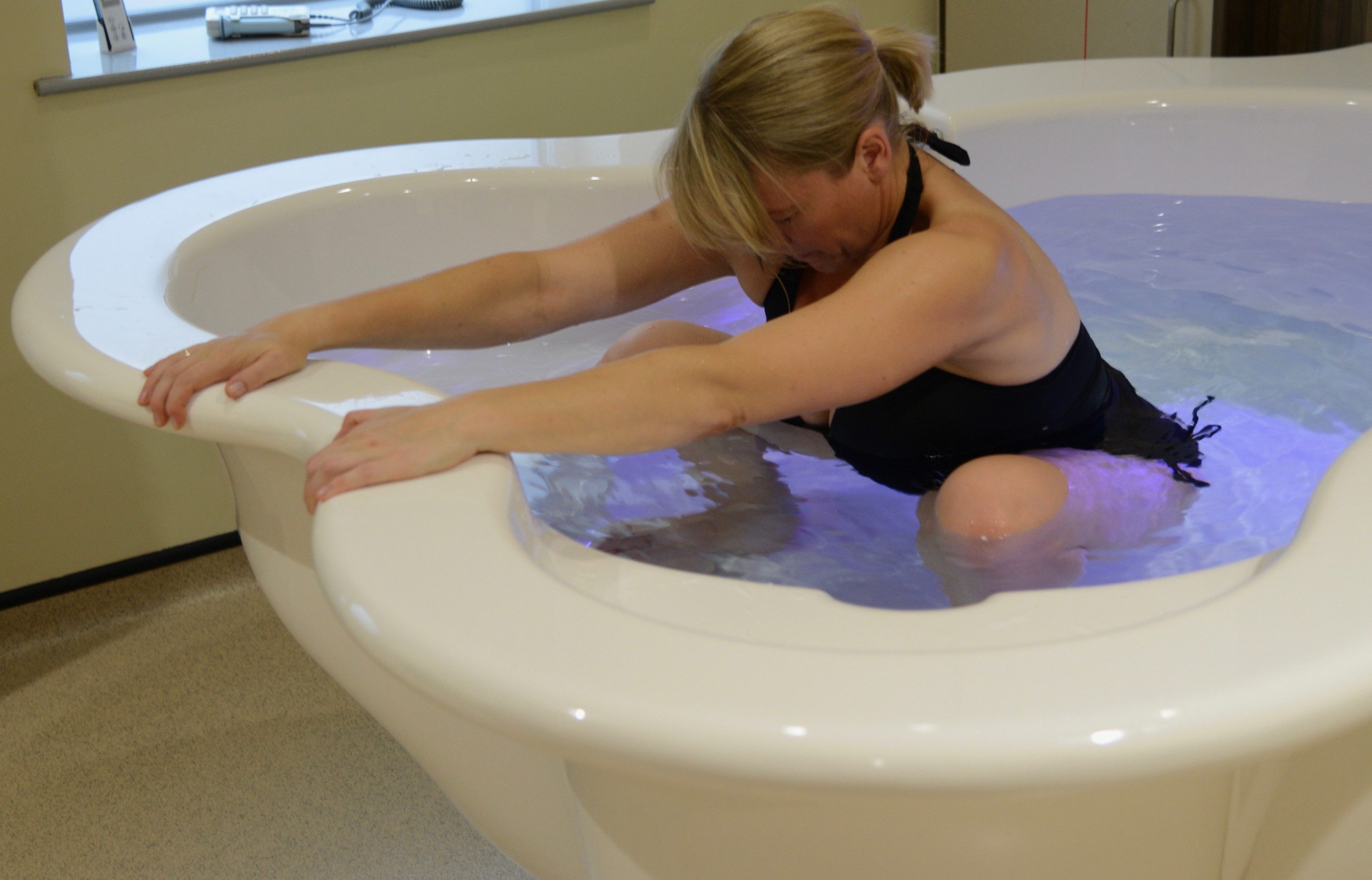
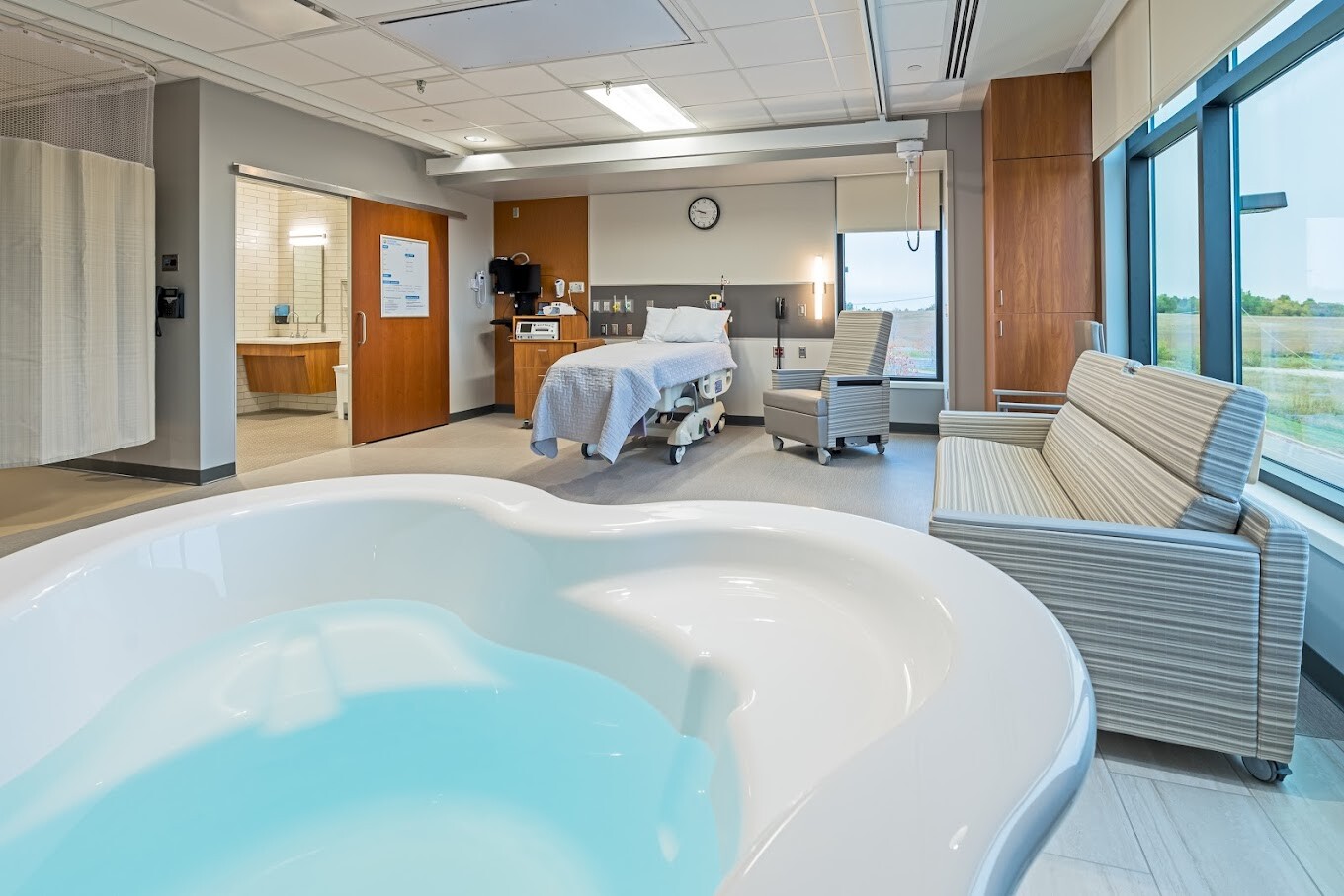
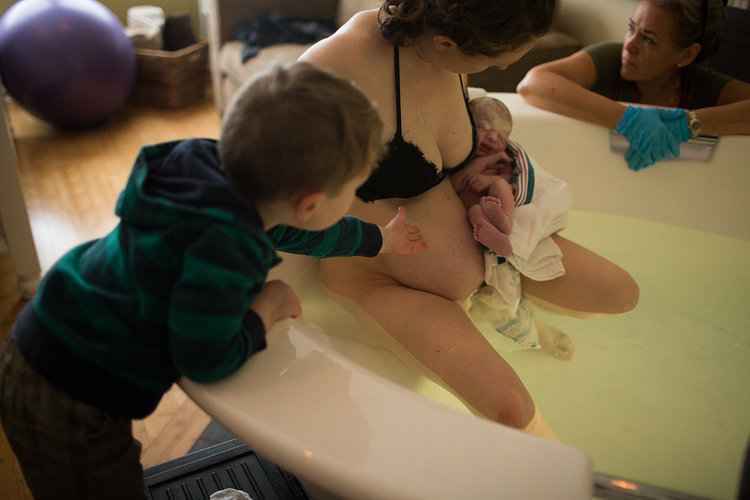
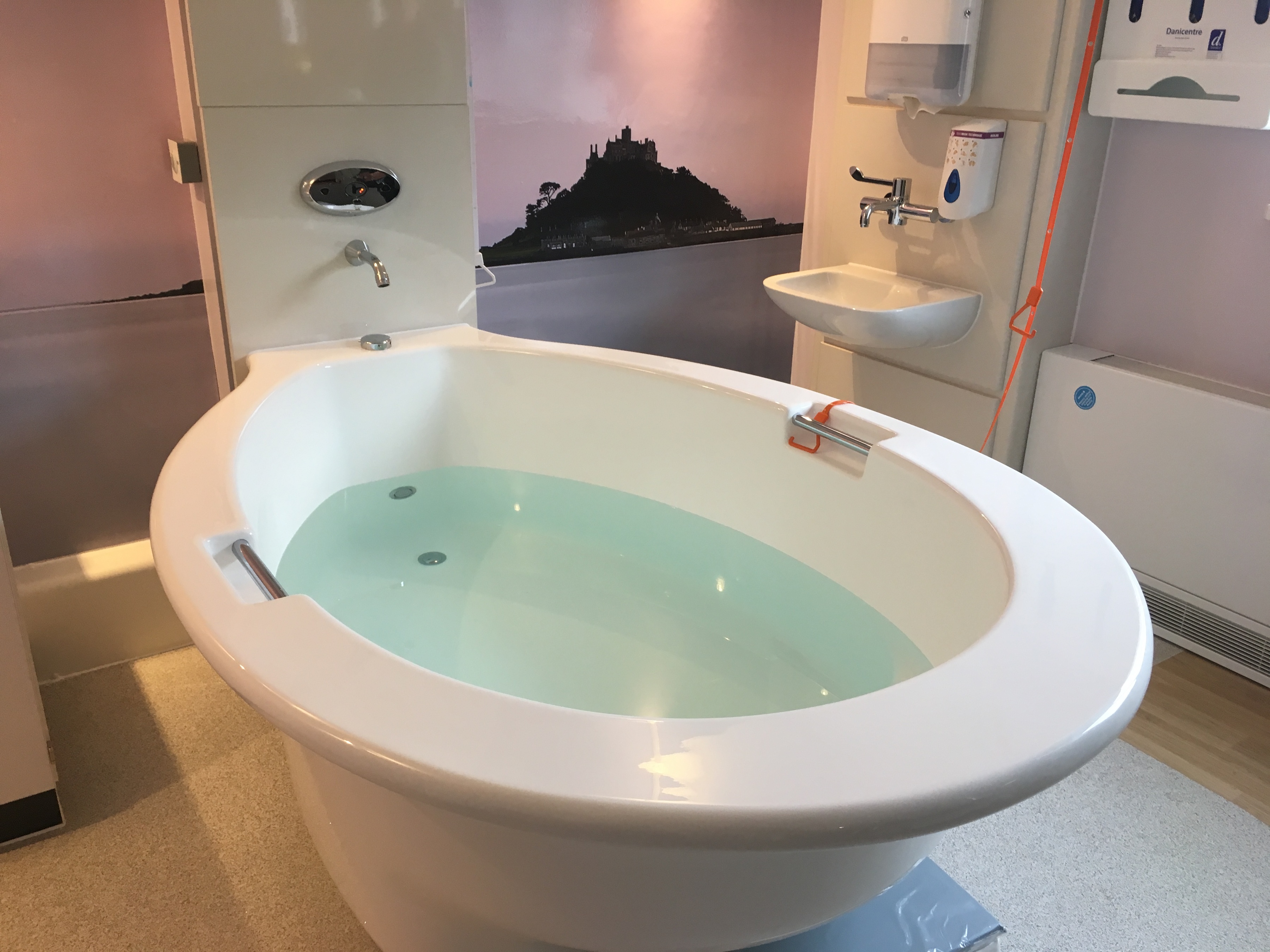
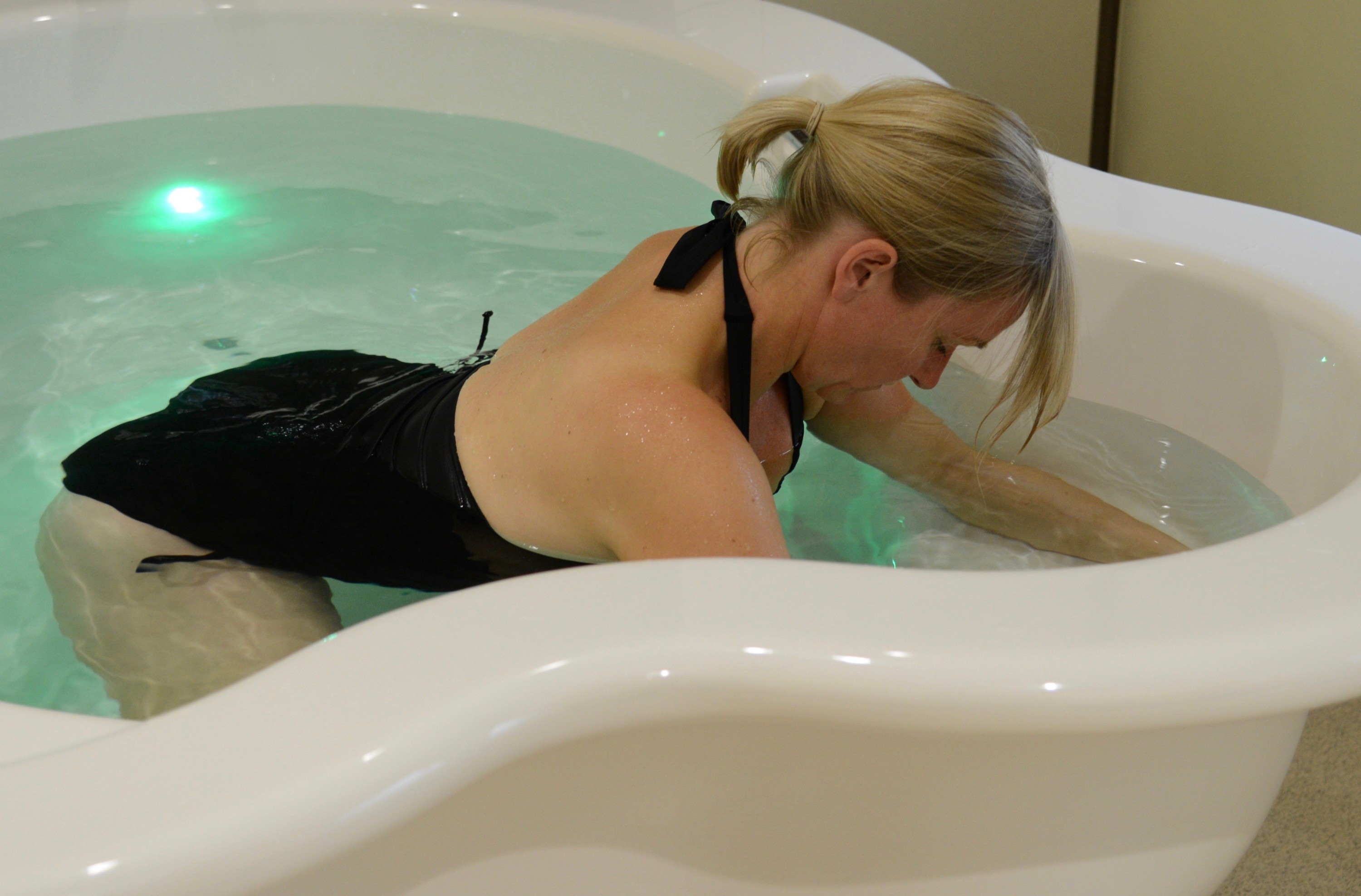
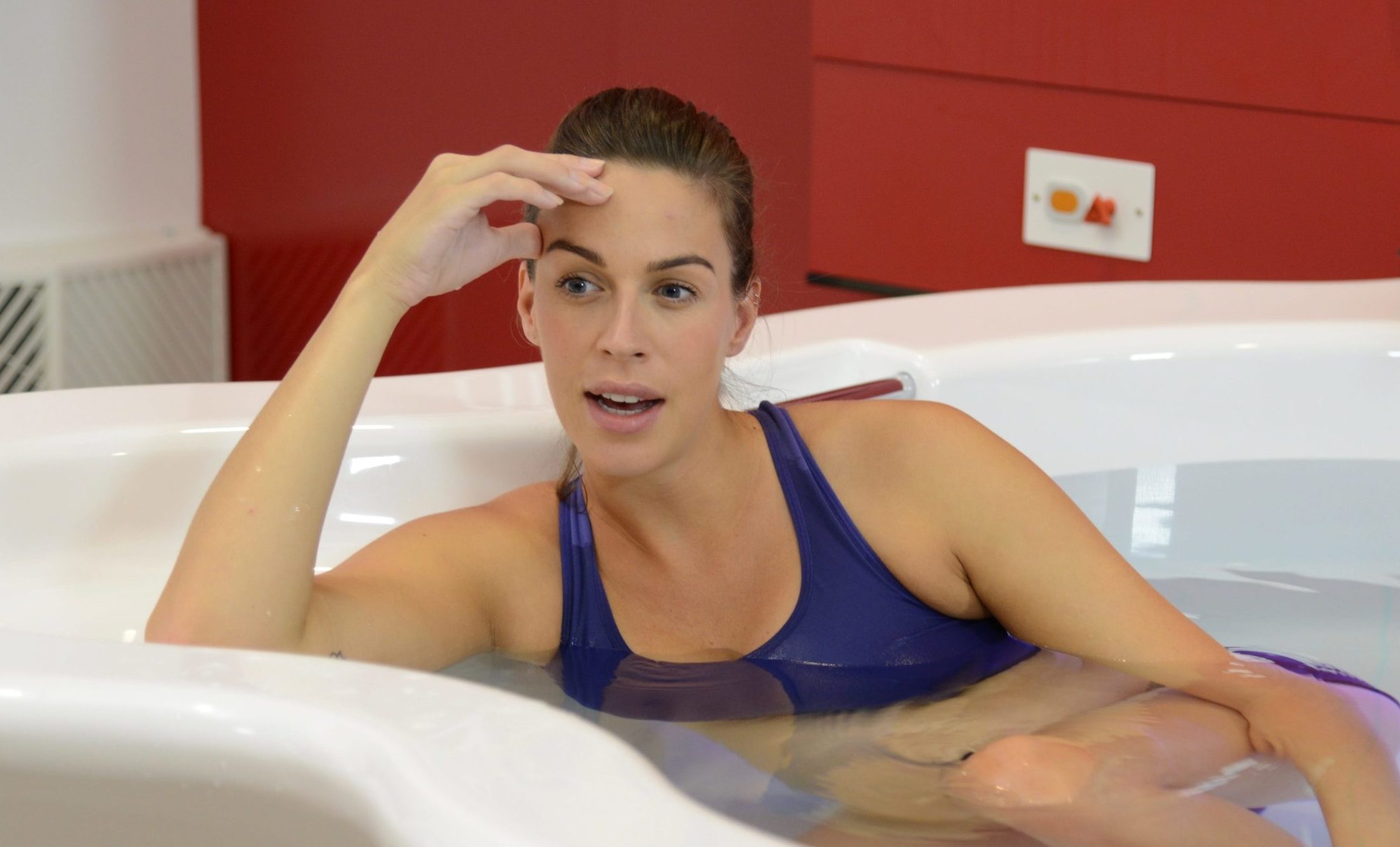
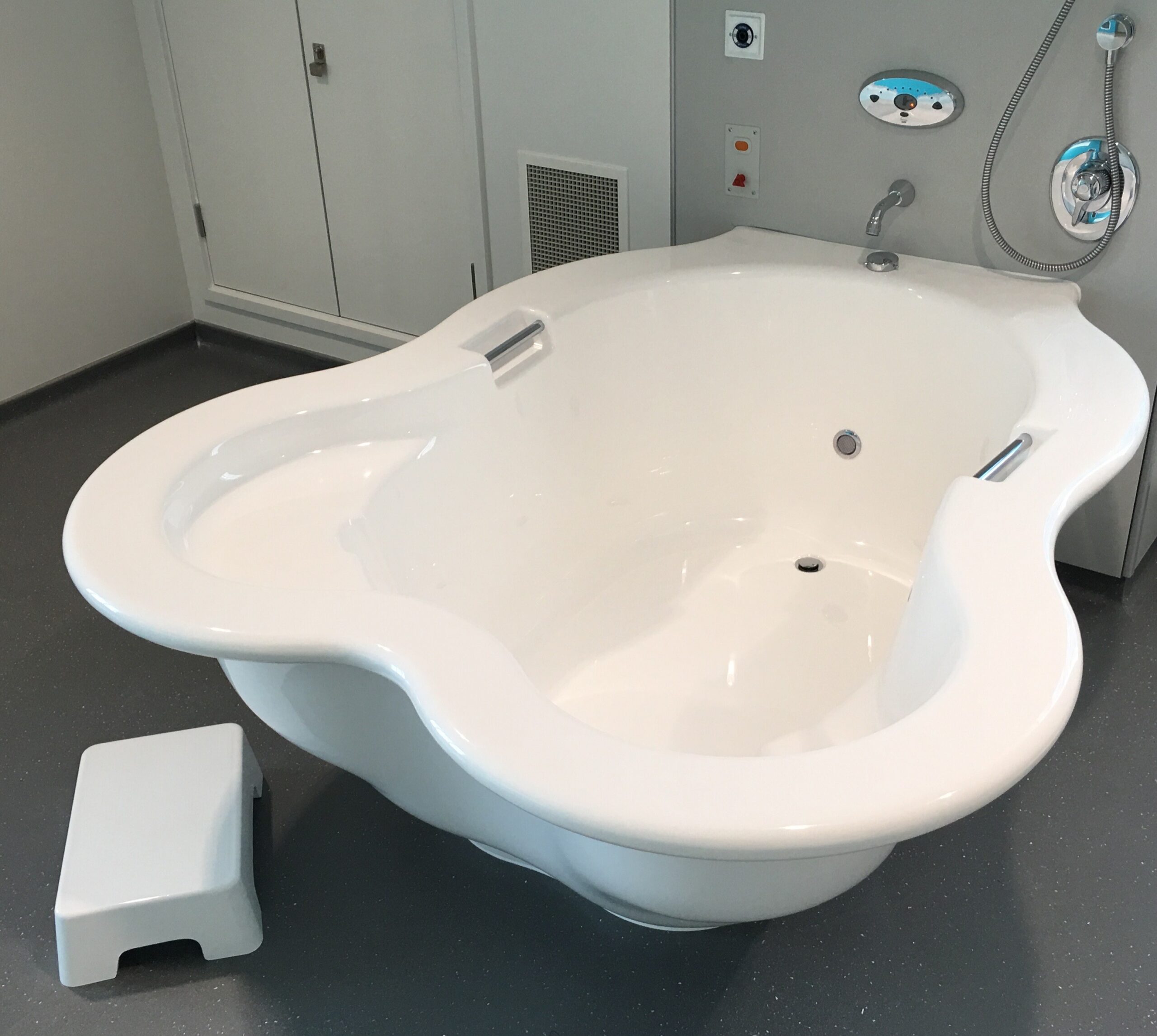
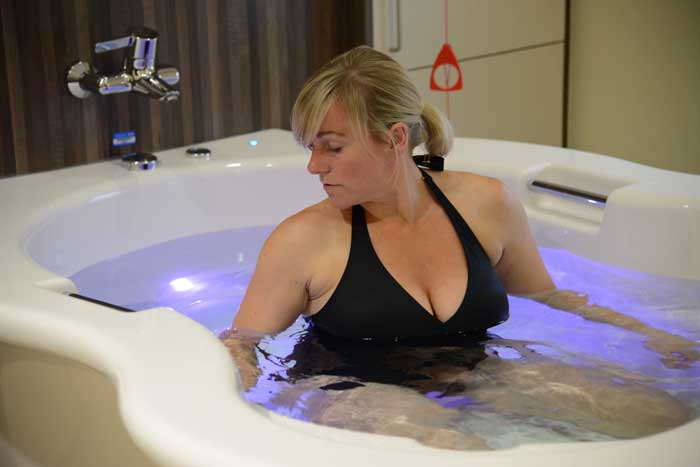
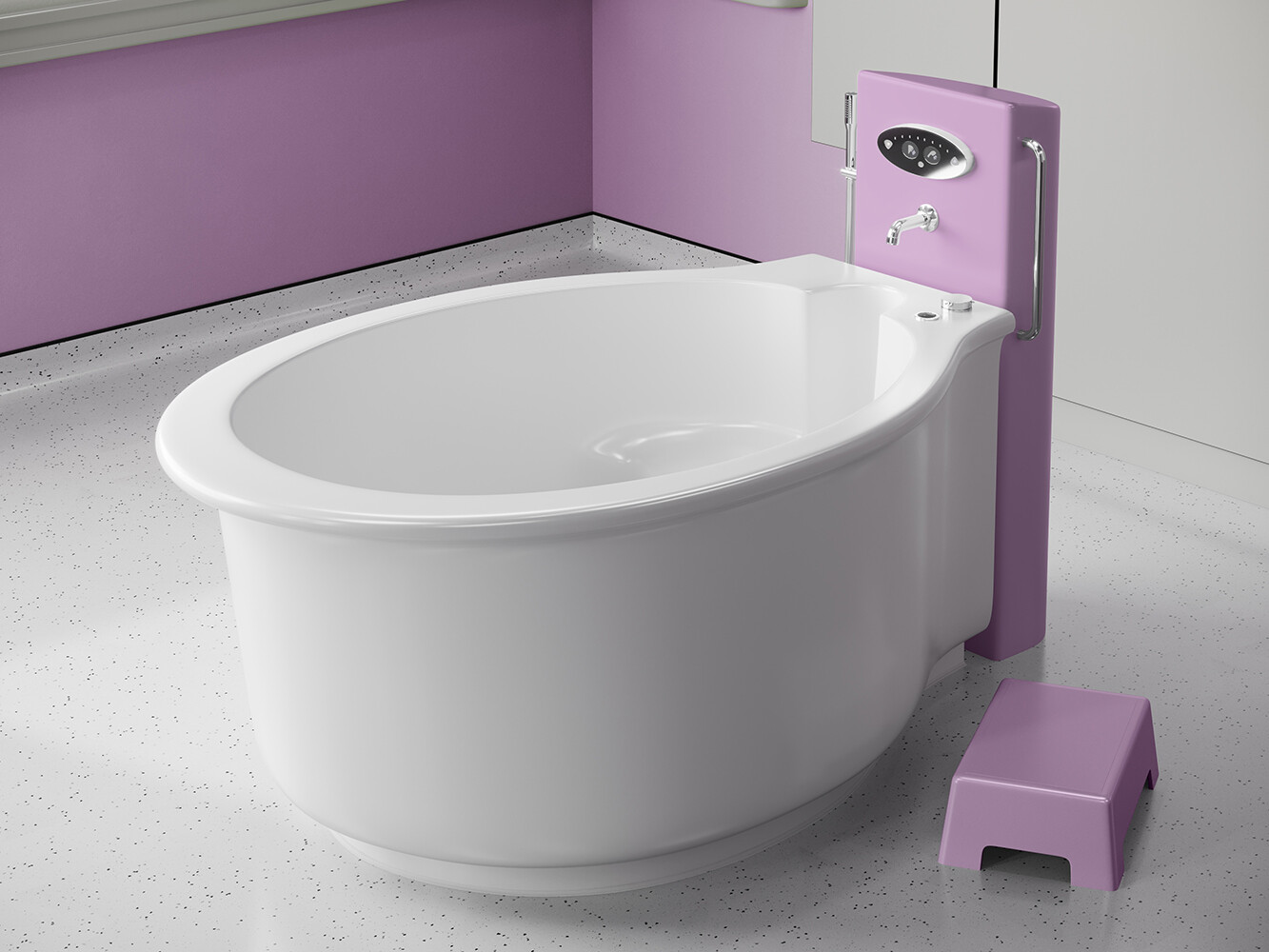
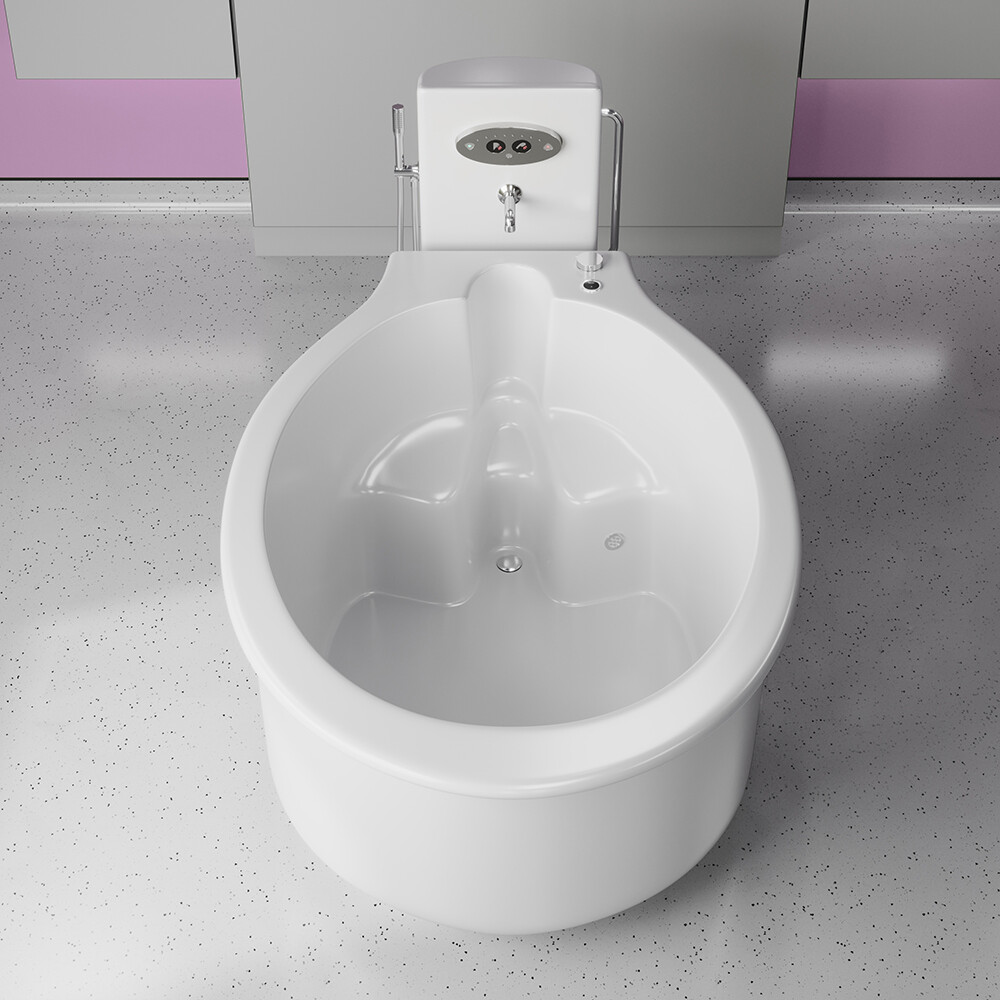
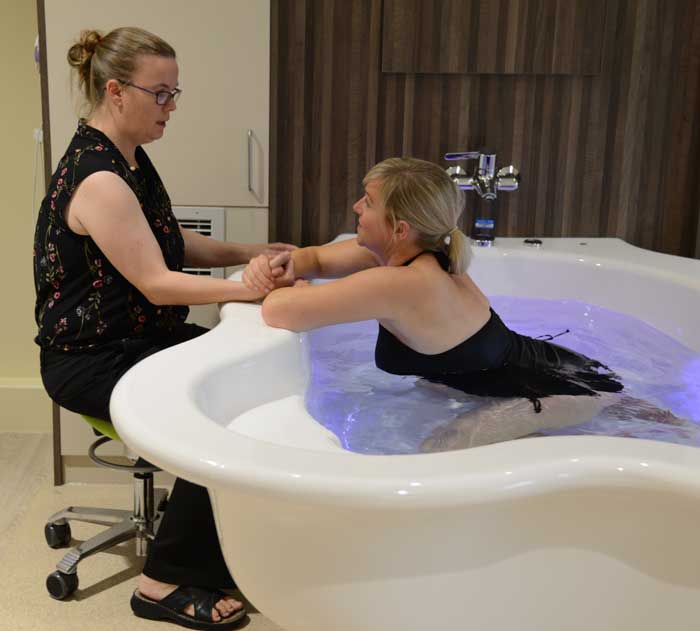
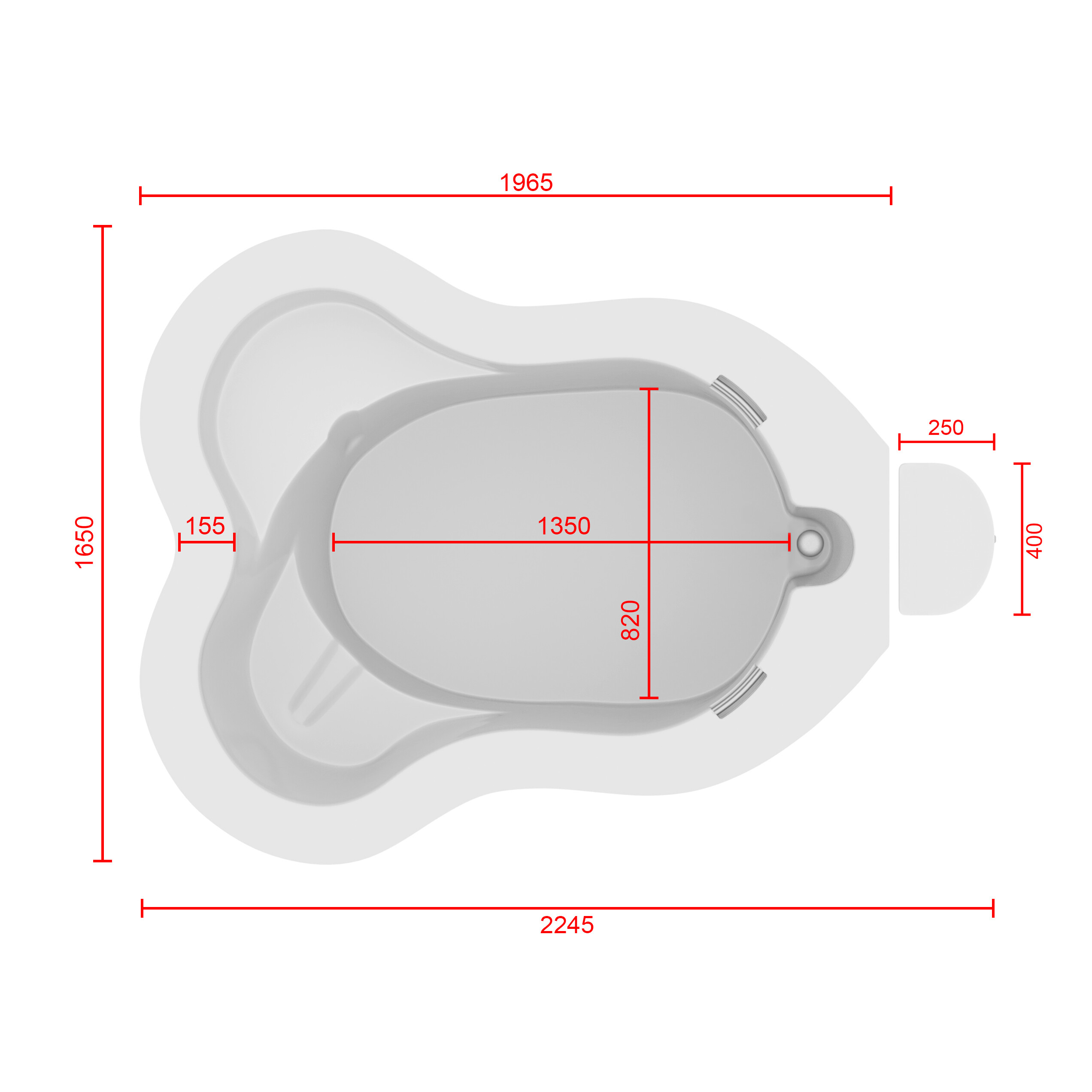
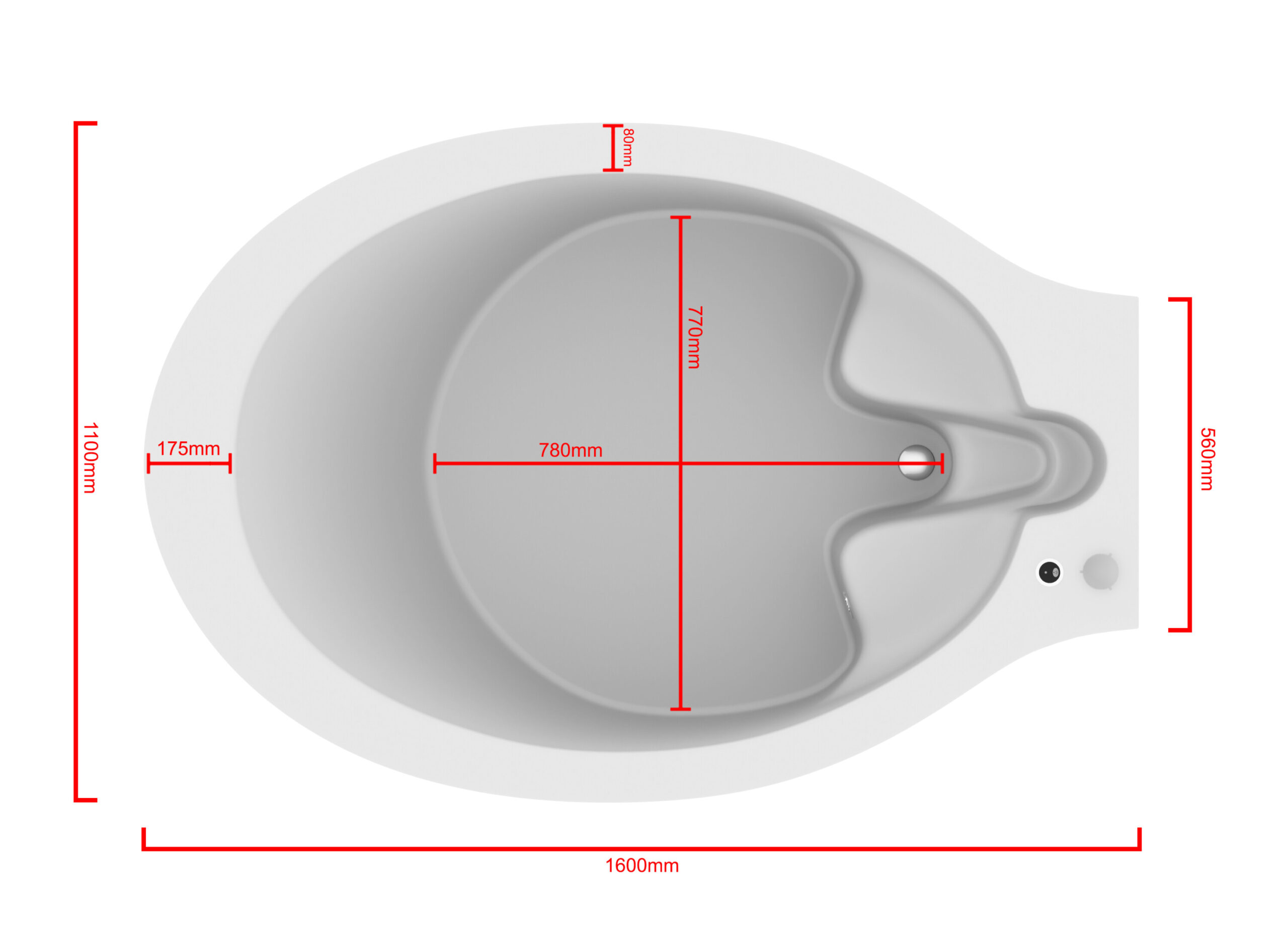
في الساحة المتطورة باستمرار لرعاية الأمومة، تسعى المستشفيات باستمرار إلى وسائل مبتكرة لتعزيز تجربة الولادة للأمهات المتوقعات. إحدى هذه الابتكارات التي تكتسب قوة هي دمج حمامات المياه خلال مرافق المستشفيات. بعيدًا عن أن تكون مجرد اتجاهٍ، تقدم حمامات المياه للولادة فوائد كثيرة لا تقتصر فقط على أولياء الأمور ولكن تساهم أيضًا في تحسين تجربة الولادة بشكل شامل وتعزيز الشعور بالتمكين. في هذا المقال، سنتناول الأسباب المقنعة التي يجب على المستشفيات أن تفكر في اعتناق هذا التوجه ودمج حمامات المياه في خدمات رعاية الأمومة الخاصة بها.
تخفيف الألم بشكل طبيعي:
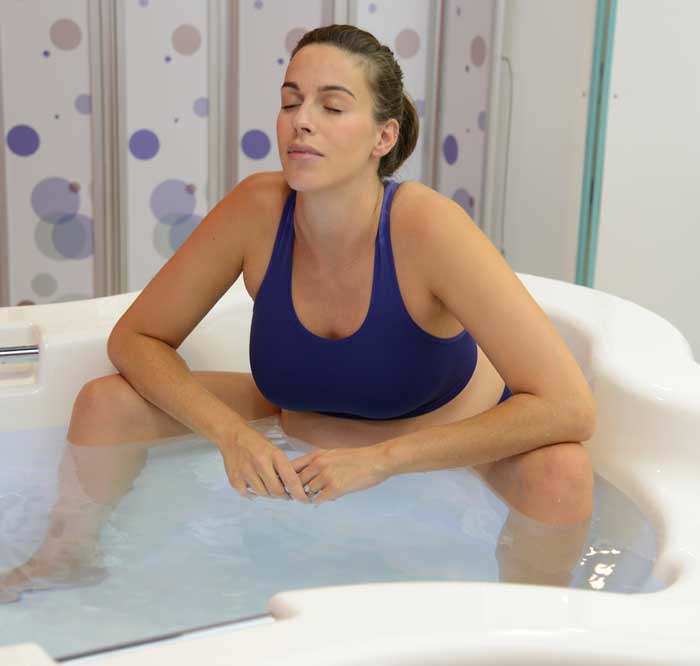
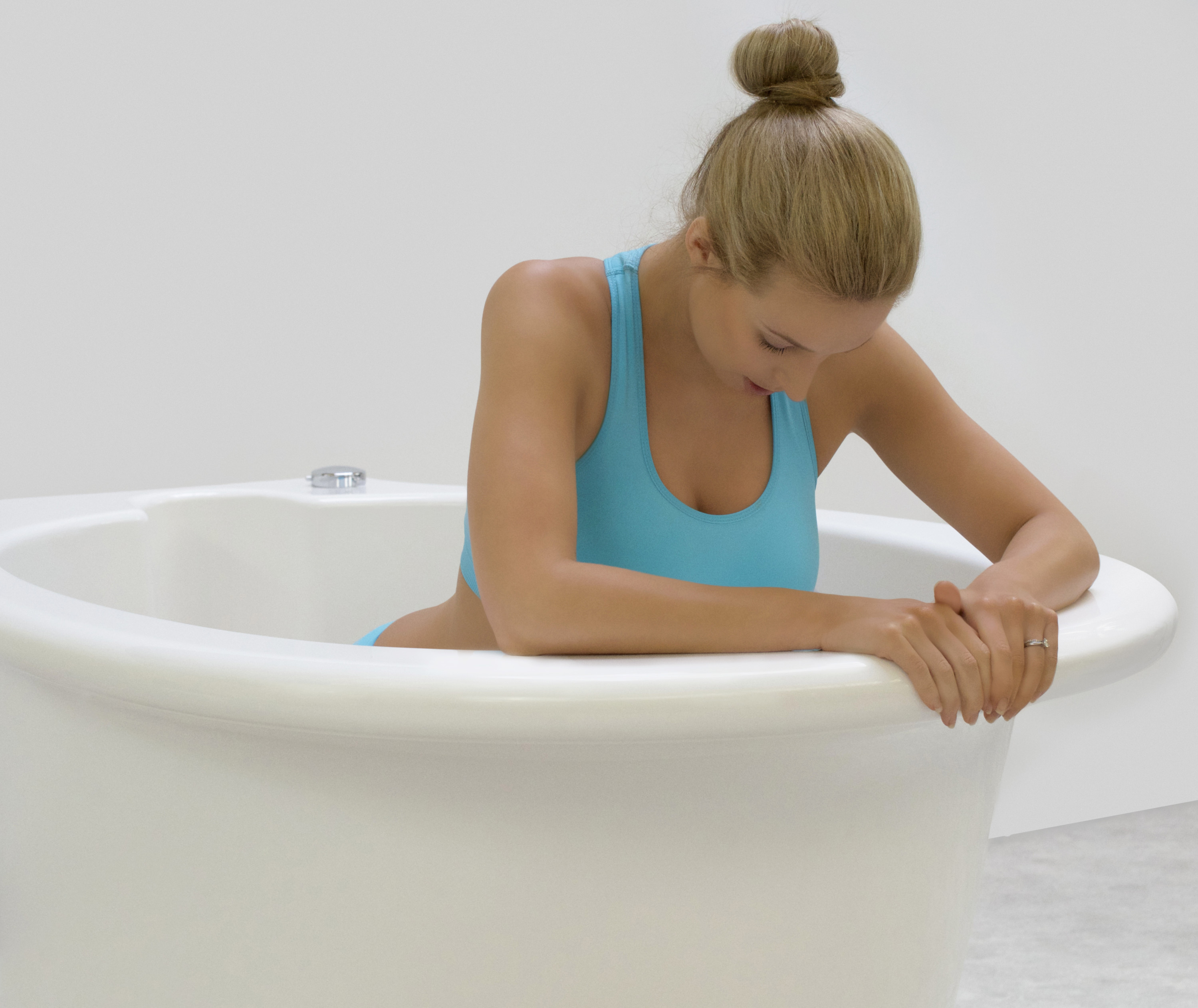
لقد تم التعرف على الماء منذ فترة طويلة كمسكن طبيعي قوي. الانغماس في الماء الدافئ يمكن أن يخفف من شدة التقلصات ويوفر إحساسًا بعدم الوزن، مما يقلل من تأثير الجاذبية على الجسم. تقدم المستشفيات التي توفر حمامات المياه للولادة للأمهات خيار إدارة الألم البديل الذي يكمل الطرق التقليدية، مما يوفر نهجًا أكثر شخصنة للراحة خلال الولادة. أظهرت العديد من الدراسات فعالية الانغماس في الماء في تخفيف ألم الولادة. خلصت مراجعة نشرت في “مجلة التعليم الأمومي” (هاربر وآخرون، 2016) إلى أن الانغماس في الماء الدافئ أثناء الولادة يقلل بشكل كبير من تصور الألم، مما يوفر للأمهات المتوقعات خيارًا لتخفيف الألم غير دوائي ومستند إلى الأدلة. تشير الأبحاث المنشورة في “مجلة التمريض النسائي والتوليدي وحديثي الولادة” (ثويني وآخرون، 2019) إلى أن الانغماس في الماء أثناء الولادة يقلل من هرمونات التوتر، مما يعزز حالة أكثر استرخاءً للأم والطفل. ربط انخفاض مستويات هرمونات التوتر بتحسين الرفاهية الأمومية والنتائج المواتية للولادة، مما يدعم الحجة لحمامات المياه كنهج شامل لرعاية الأمومة.

تقليل التوتر والقلق:
يمكن أن يكون عملية الولادة مصدر قلق للعديد من الأمهات المتوقعات. تخلق حمامات المياه للولادة بيئة هادئة ومهدئة، تعزز الاسترخاء وتقلل من مستويات التوتر. تعزز الطفو في الماء إحساسًا بعدم الوزن، مما يسمح للأمهات بالحركة بحرية أكبر وتبني وضعيات مريحة، مما يسهم في تجربة ولادة إيجابية وممكنة بشكل أكبر. تشير الأبحاث المنشورة في “مجلة التمريض النسائي والتوليدي وحديثي الولادة” (ثويني وآخرون، 2019) إلى أن الانغماس في الماء أثناء الولادة يقلل من هرمونات التوتر، مما يعزز حالة أكثر استرخاءً للأم والطفل. رُبطت مستويات منخفضة لهرمونات التوتر بتحسين الرفاهية الأمومية والنتائج المواتية للولادة، مما يدعم الحجة لحمامات المياه كنهج شامل لرعاية الأمومة.

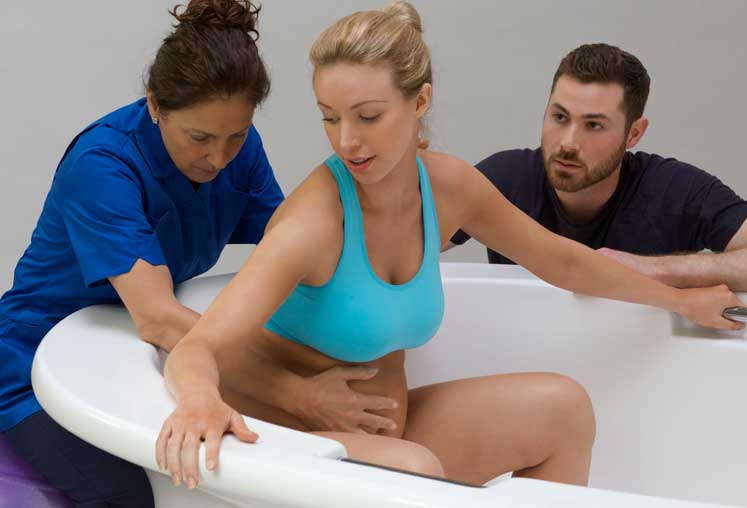
تسهيل الحركة والتوجيه:
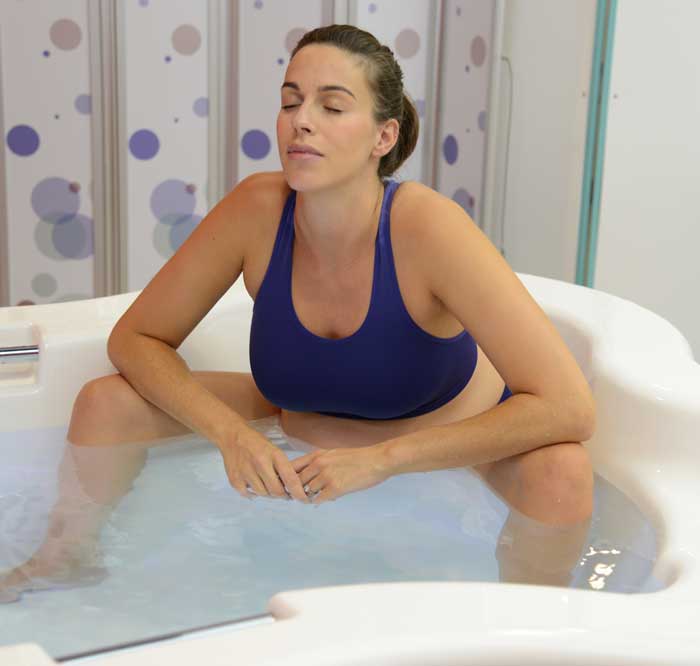
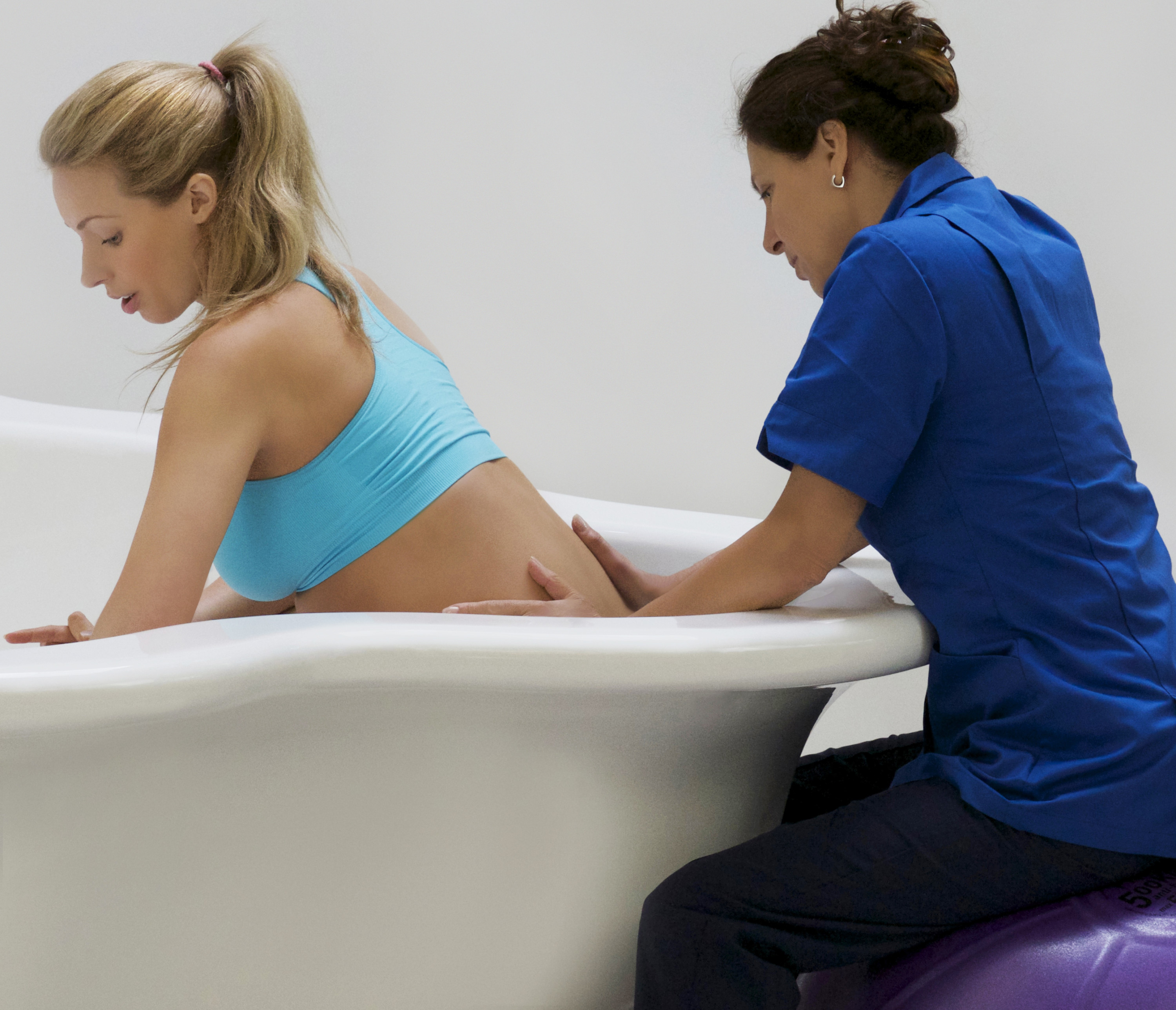
توفر حمامات المياه للولادة بيئة تسهل الحركة والتوجيه خلال عملية الولادة. يسمح الطفو بزيادة القدرة على الحركة، مما يتيح للأمهات تغيير وضعياتهن بسهولة والعثور على أكثر وضع مريح للولادة. يمكن أن تعزز هذه المرونة تقدم عملية الولادة وتسهل عملية الولادة. أظهرت دراسة نشرت في “المجلة الأمريكية لطب النساء والتوليد” (زانيتي-دالينباخ وآخرون، 2007) أن الانغماس في الماء يعزز القدرة على الحركة لدى الأمهات خلال الولادة. يسمح طفو الماء بحركة وتوجيه أسهل، مما قد يقلل من مدة الولادة ويقلل من الحاجة إلى التدخلات. تؤكد هذه الأدلة على أهمية حمامات المياه في توفير بيئة تسهل التوجيه الأمثل لعملية الولادة.

تحسين الدورة الدموية:
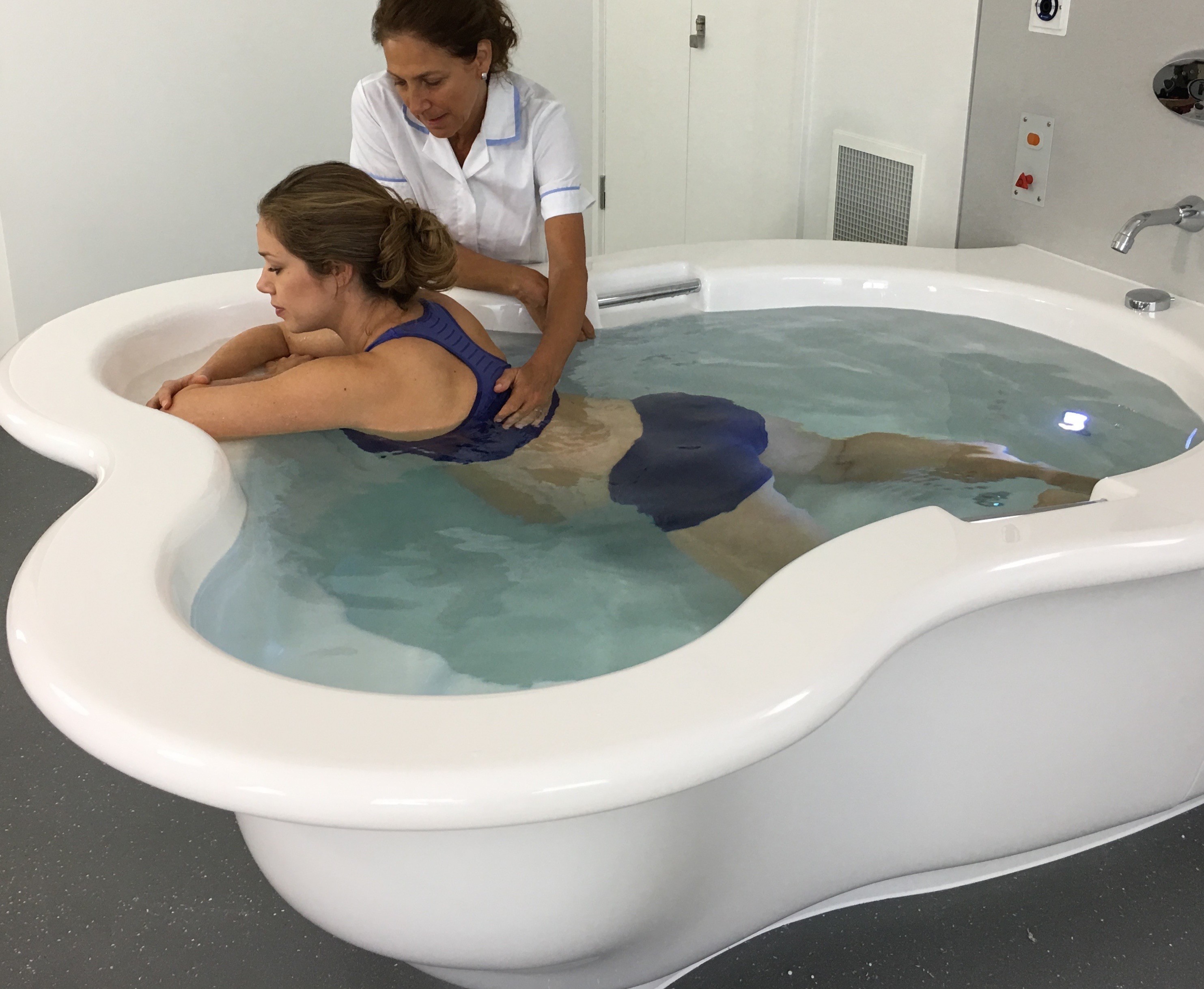
الماء الدافئ في حمام الولادة يعزز تحسين الدورة الدموية، وهو ما يمكن أن يكون مفيدًا بشكل خاص خلال عملية الولادة. تساعد التداول المحسّن في التقليل من الانتفاخ وتعزيز تدفق الأكسجين، مما يسهم في رفاهية الأم والطفل على حد سواء. تعتبر المستشفيات التي تدمج حمامات المياه للولادة أولوية للجوانب الفسيولوجية للولادة، معززة بذلك بيئة ولادة أكثر صحة. لقد تم توثيق التأثير الإيجابي للانغماس في الماء الدافئ على الدورة الدموية بشكل جيد. أظهرت دراسة سيطرية عشوائية نشرت في “مجلة القابلات وصحة المرأة” (بيرنز وآخرون، 2012) أن الانغماس في الماء الدافئ يزيد من تدفق الدم في الأطراف وتأكسجها، مما يوفر فوائد فسيولوجية تسهم في الرفاه العام للأم والطفل.
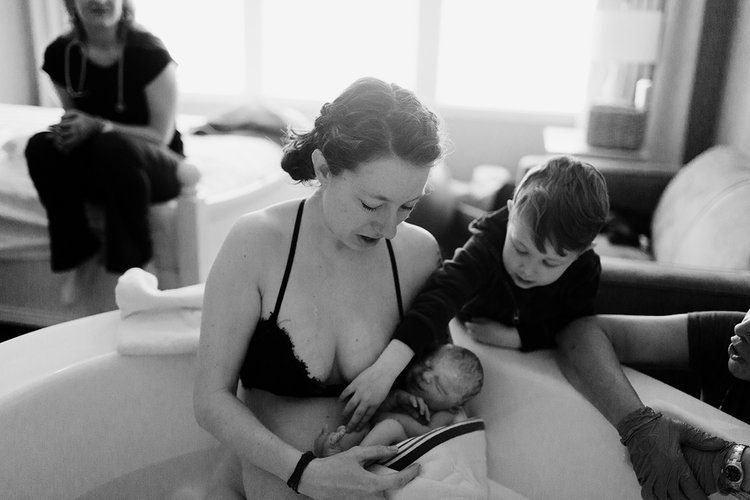

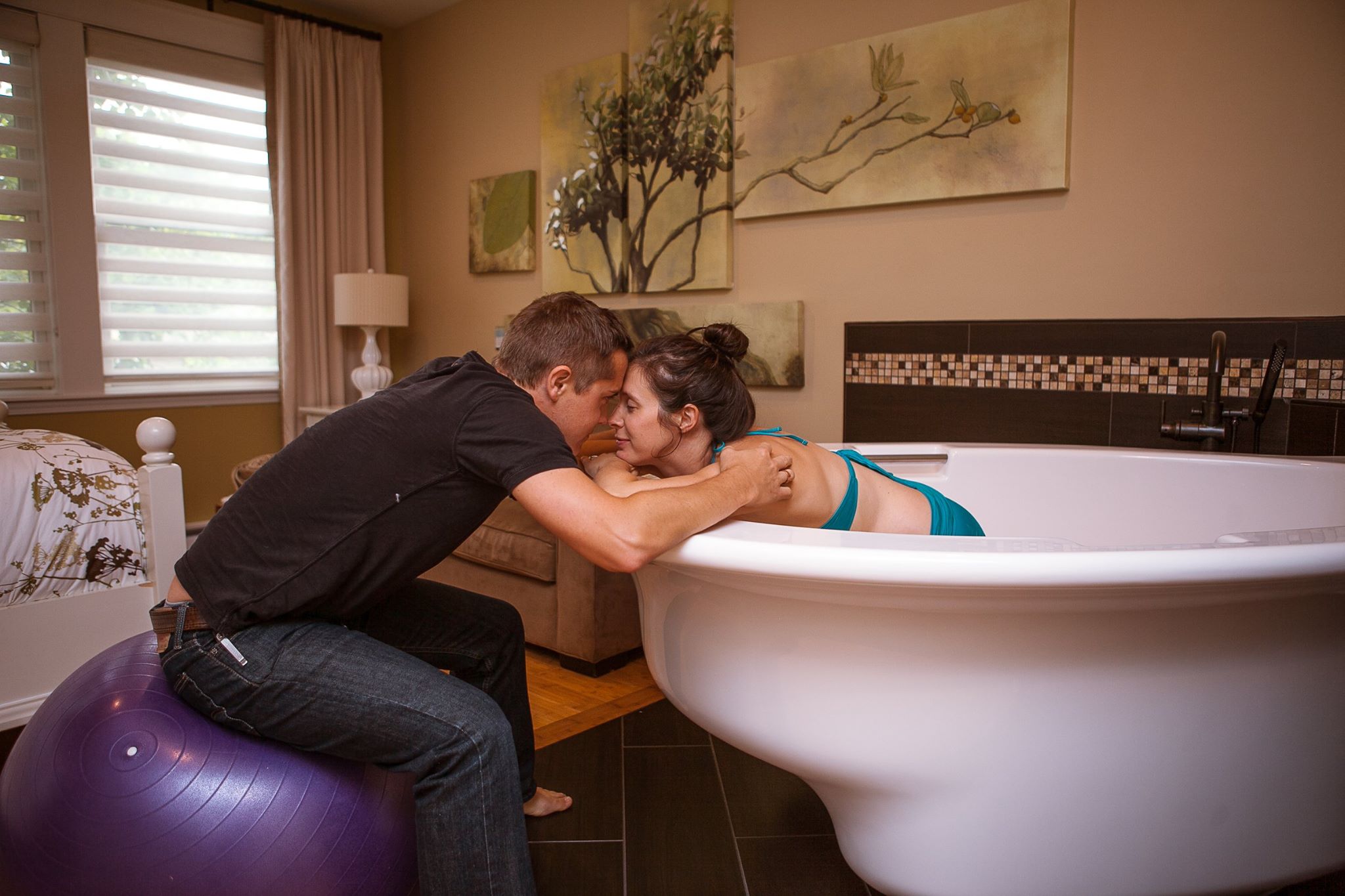
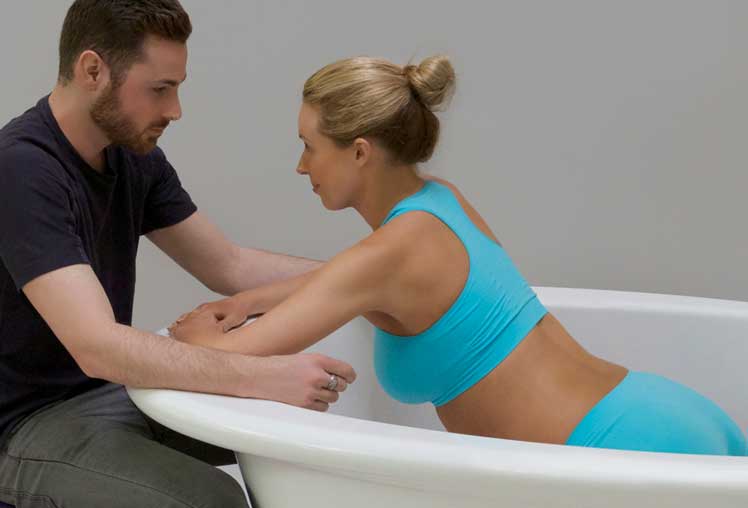
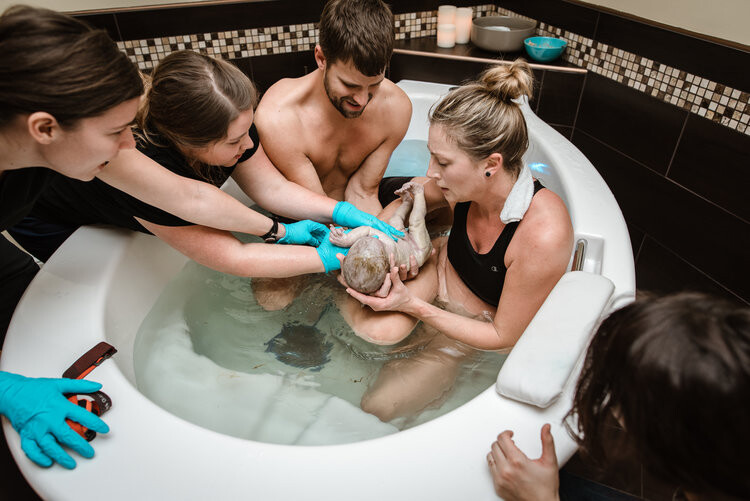
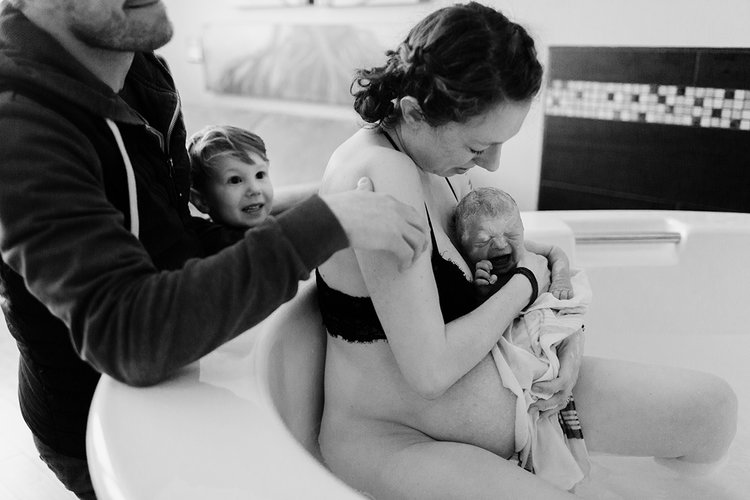
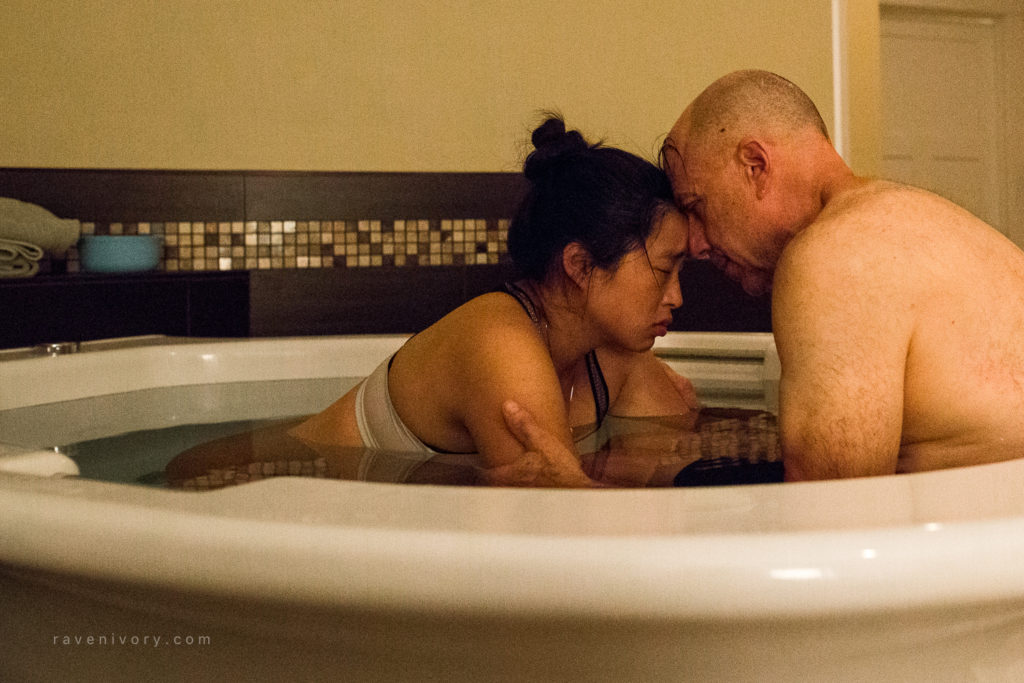
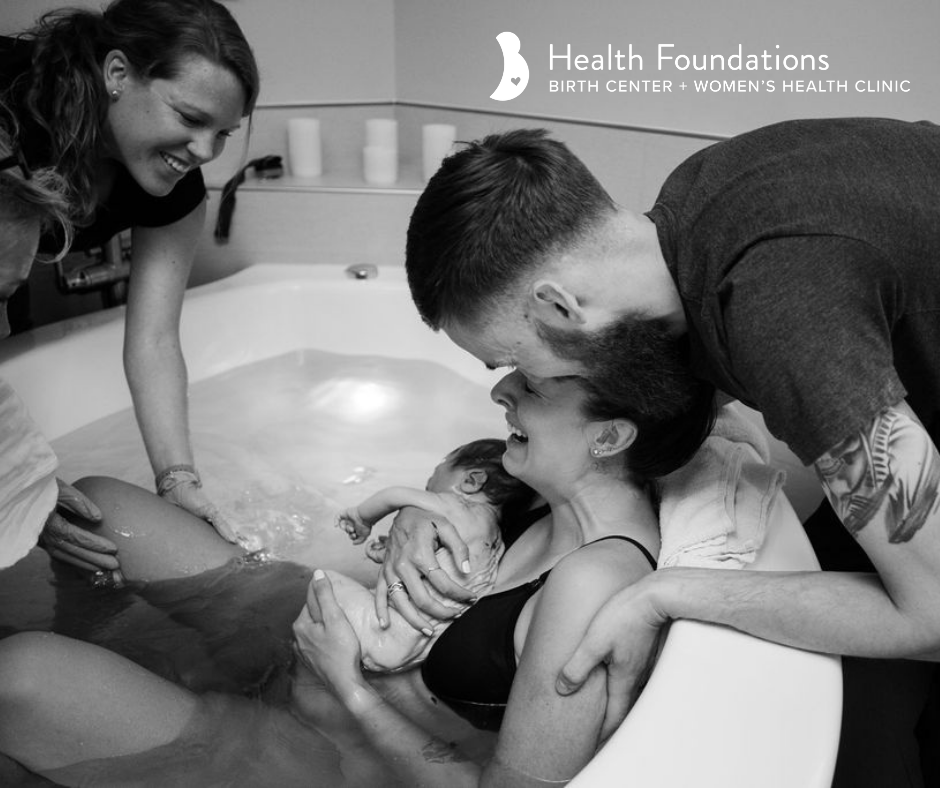
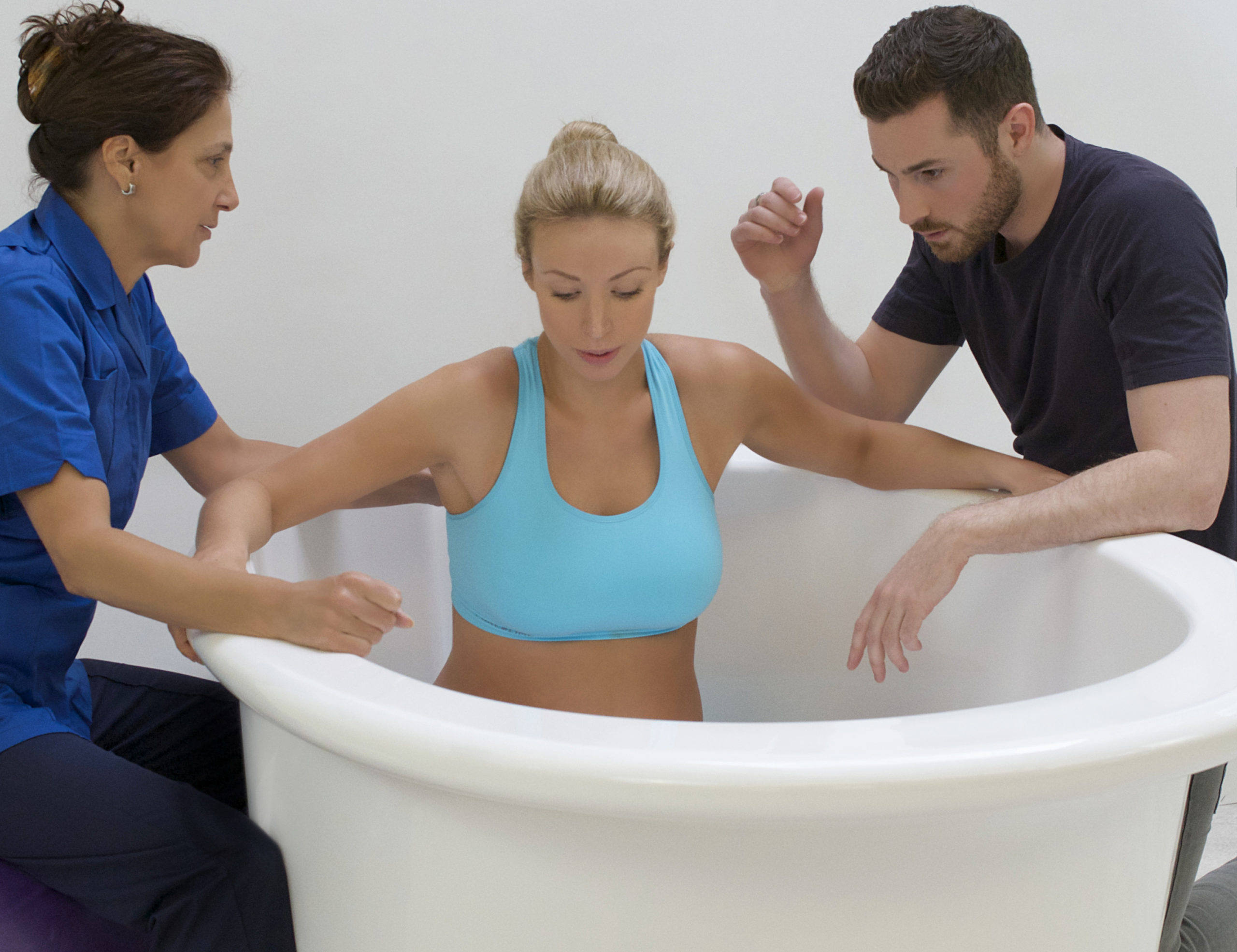
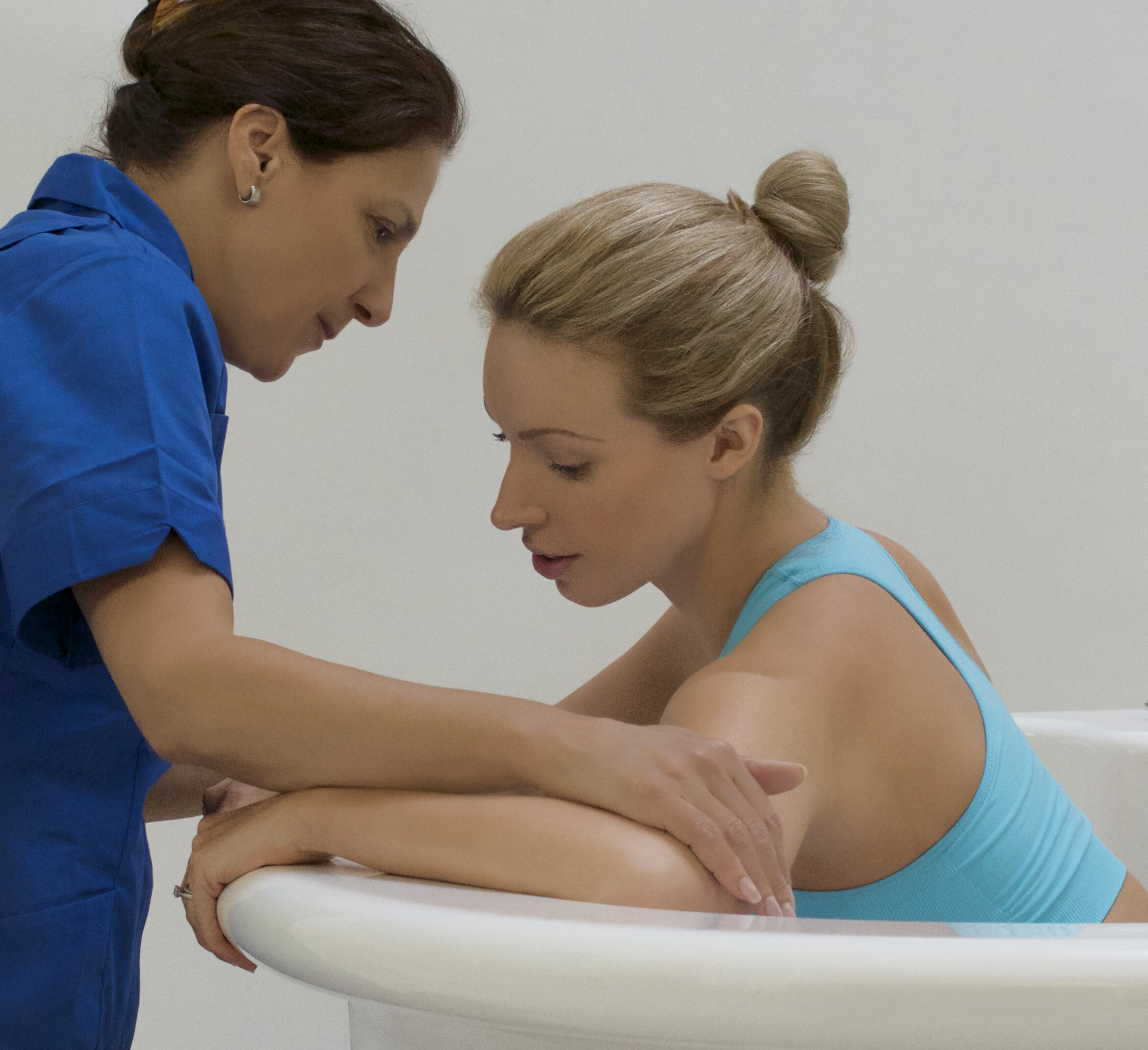
تعزيز الرباط:
الإعداد الحميم والخاص لحمام الولادة يشجع على مشاركة الشريك ويعزز الرباط الأعمق بين الآباء والمولود الجديد. تجربة الولادة المشتركة في حمام الولادة يمكن أن تعزز الرابط العاطفي بين الشركاء، معززةً الشعور بالوحدة والمسؤولية المشتركة في استقبال أحدث أفراد العائلة. أجريت دراسة شاملة للميتا نشرت في “مجلة الولادة: قضايا الرعاية خلال فترة ما بعد الولادة” (نيكوديم وآخرون، 2016) لفحص النتائج النفسية للانغماس في الماء أثناء الولادة. أظهر التحليل وجود ترابط إيجابي بين تجارب الولادة في الماء وزيادة الرضا الأمومي والرباط مع المولود الجديد.

ختام:
المستشفيات التي تعتبر إدماج حمامات المياه للولادة أولوية تتماشى مع الأدلة التي تدعم الفوائد العاطفية لهذا النهج في الولادة. إدماج حمامات المياه في خدمات الرعاية بالمستشفى للأمومة يمثل خطوة تقدمية نحو توفير نهج أكثر شمولًا وتركيزًا على المريض في عملية الولادة. فوق الفوائد الجسدية، مثل تخفيف الألم الطبيعي وتحسين الدورة الدموية، تساهم حمامات المياه للولادة في تحسين تجربة عاطفية أكثر غنى للوالدين. مع سعي المستشفيات للأولوية لرفاهية وتفضيلات الأمهات المتوقعات، يظهر إدماج حمامات المياه كخيار مقنع، مستذكرًا الارتباط القديم بين الإنسانية وضمان الماء المهدئ خلال معجزة الولادة. إدماج حمامات المياه في خدمات الرعاية بالمستشفى للأمومة ليس مجرد خطوة تقدمية؛ بل هو قفزة مدعومة علميا نحو توفير تجارب الولادة القائمة على الأدلة ومحورة حول المريض. تعزيز فوائد الانغماس في الماء خلال الولادة من خلال العديد من الدراسات يعزز الفكرة بأنه يجب على المستشفيات أن تعتبر حمامات المياه للولادة ليست فاخرة بل عنصرًا حيويًا في تعزيز بيئة ولادة آمنة ومريحة وقائمة على الأدلة. إن جمود الأدلة يدعم بقوة إدماج حمامات المياه كقوة محولة في رعاية الأمومة الحديثة.
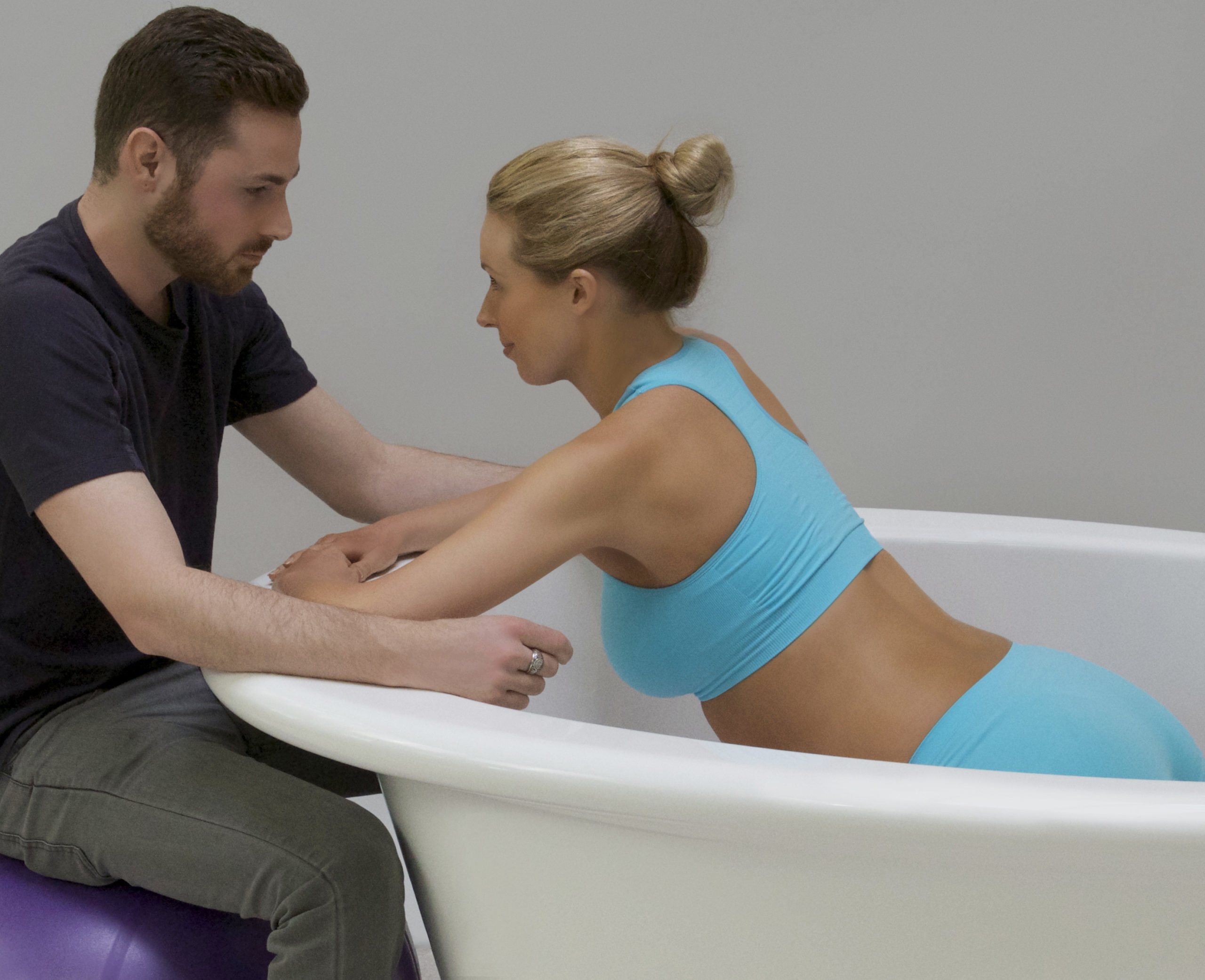
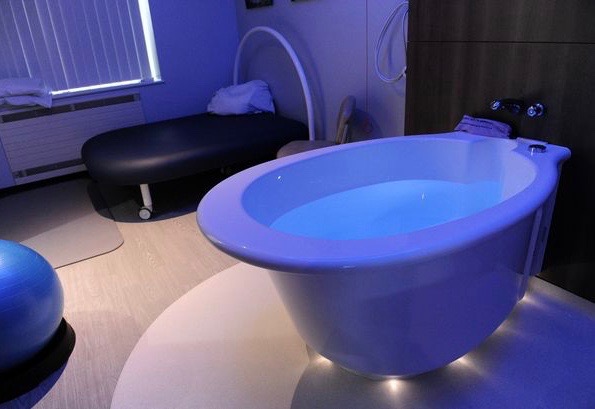
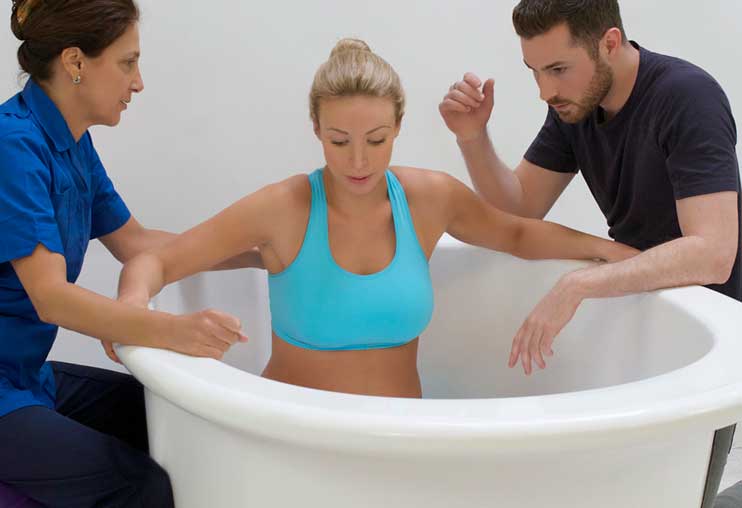




















































 Posicione o cursor sobre o modelo abaixo para mover a imagem ao redor.
Posicione o cursor sobre o modelo abaixo para mover a imagem ao redor.